三个主要组成部分
在 Java Agent 对应的 .jar 文件里,有三个主要组成部分:
- Manifest
- Agent Class
- ClassFileTransformer
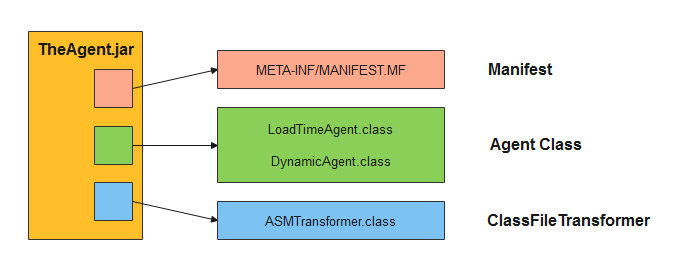
┌─── Manifest ───────────────┼─── META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
│
│ ┌─── LoadTimeAgent.class: premain
TheAgent.jar ───┼─── Agent Class ────────────┤
│ └─── DynamicAgent.class: agentmain
│
└─── ClassFileTransformer ───┼─── ASMTransformer.class
Manifest Attributes
首先,在 Manifest 文件当中,可以定义的属性非常多,但是与 Java Agent 相关的属性有 6、7 个。
- 在 Java 8 版本当中,定义的属性有 6 个;
- 在 Java 9 至 Java 17 版本当中,定义的属性有 7 个。
其中,
Launcher-Agent-Class属性,是 Java 9 引入的。
其次,我们将 Manifest 定义的属性分成了三组:基础、能力和特殊情况。
┌─── Premain-Class
┌─── Basic ─────┤
│ └─── Agent-Class
│
│ ┌─── Can-Redefine-Classes
│ │
Manifest Attributes ───┼─── Ability ───┼─── Can-Retransform-Classes
│ │
│ └─── Can-Set-Native-Method-Prefix
│
│ ┌─── Boot-Class-Path
└─── Special ───┤
└─── Launcher-Agent-Class
分组的目的,是为了便于理解:一下子记住 7 个属性,不太容易;分成三组,每次记忆两、三个属性,就相对容易一些。
这些分组,也对应着先、后的学习顺序,它也是由简单到复杂的过程。
注意:这个分组是我个人的理解,并不一定是对的。如果你有更好的认知方式,可以按自己的思路来。
基础
An attribute in the JAR file manifest specifies the agent class which will be loaded to start the agent.
Premain-Class: When an agent is specified at JVM launch time this attribute specifies the agent class. That is, the class containing thepremainmethod. When an agent is specified at JVM launch time this attribute is required. If the attribute is not present the JVM will abort. Note: this is a class name, not a file name or path.Agent-Class: If an implementation supports a mechanism to start agents sometime after the VM has started then this attribute specifies the agent class. That is, the class containing theagentmainmethod. This attribute is required, if it is not present the agent will not be started. Note: this is a class name, not a file name or path.
Premain-Class: lsieun.agent.LoadTimeAgent
Agent-Class: lsieun.agent.DynamicAgent
An agent JAR file may have both the Premain-Class and Agent-Class attributes present in the manifest.
- When the agent is started on the command-line using the
-javaagentoption then thePremain-Classattribute specifies the name of the agent class and theAgent-Classattribute is ignored. - Similarly, if the agent is started sometime after the VM has started,
then the
Agent-Classattribute specifies the name of the agent class (the value ofPremain-Classattribute is ignored).
能力
能力,体现在两个层面上:JVM 和 Java Agent。
┌─── redefine
│
┌─── Java Agent ───┼─── retransform
│ │
│ └─── native method prefix
Ability ───┤
│ ┌─── redefine
│ │
└─── JVM ──────────┼─── retransform
│
└─── native method prefix
下面三个属性,就是确定 Java Agent 的能力:
Can-Redefine-Classes: Boolean (trueorfalse, case irrelevant).- Is the ability to redefine classes needed by this agent.
- Values other than
trueare consideredfalse. - This attribute is optional, the default is
false.
Can-Retransform-Classes: Boolean (trueorfalse, case irrelevant).- Is the ability to retransform classes needed by this agent.
- Values other than
trueare consideredfalse. - This attribute is optional, the default is
false.
Can-Set-Native-Method-Prefix: Boolean (trueorfalse, case irrelevant).- Is the ability to set native method prefix needed by this agent.
- Values other
thantrue are consideredfalse. - This attribute is optional, the default is
false.
特殊情况
Boot-Class-Path: A list of paths to be searched by the bootstrap class loader. Paths represent directories or libraries (commonly referred to as JAR or zip libraries on many platforms). These paths are searched by the bootstrap class loader after the platform specific mechanisms of locating a class have failed. Paths are searched in the order listed. Paths in the list are separated by one or more spaces. A path takes the syntax of the path component of a hierarchical URI. The path is absolute if it begins with a slash character (/), otherwise it is relative. A relative path is resolved against the absolute path of the agent JAR file. Malformed and non-existent paths are ignored. When an agent is started sometime after the VM has started then paths that do not represent a JAR file are ignored. This attribute is optional.Launcher-Agent-Class: If an implementation supports a mechanism to start an application as an executable JAR then the main manifest may include this attribute to specify the class name of an agent to start before the applicationmainmethod is invoked.
Agent Class
LoadTimeAgent
如果我们想使用 Load-Time Instrumentation,那么就必须有一个 premain 方法,它有两种写法。
The JVM first attempts to invoke the following method on the agent class:(推荐使用)
public static void premain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation inst);
If the agent class does not implement this method then the JVM will attempt to invoke:
public static void premain(String agentArgs);
DynamicAgent
如果我们想使用 Dynamic Instrumentation,那么就必须有一个 agentmain 方法,它有两种写法。
The JVM first attempts to invoke the following method on the agent class:(推荐使用)
public static void agentmain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation inst);
If the agent class does not implement this method then the JVM will attempt to invoke:
public static void agentmain(String agentArgs);
ClassFileTransformer
在 java.lang.instrument 下包含了 Instrumentation 和 ClassFileTransformer 接口:
java.lang.instrument.Instrumentationjava.lang.instrument.ClassFileTransformer
在 Instrumentation 接口中,定义了添加和移除 ClassFileTransformer 的方法:
public interface Instrumentation {
void addTransformer(ClassFileTransformer transformer, boolean canRetransform);
boolean removeTransformer(ClassFileTransformer transformer);
}
在 ClassFileTransformer 接口中,定义了 transform 抽象方法:
public interface ClassFileTransformer {
byte[] transform(ClassLoader loader,
String className,
Class<?> classBeingRedefined,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain,
byte[] classfileBuffer) throws IllegalClassFormatException;
}
当我们想对 Class 进行 bytecode instrumentation 时,就要实现 ClassFileTransformer 接口,并重写它的 transform 方法。
总结
本文内容总结如下:
- 第一点,了解 Agent Jar 的三个主要组成部分:Manifest、Agent Class 和 ClassFileTransformer。
- 第二点,在 Agent Jar 当中,这些不同的组成部分之间是如何联系在一起的。
Manifest --> Agent Class --> Instrumentation --> ClassFileTransformer
