Attach API
在进行 Dynamic Instrumentation 的时候,我们需要用到 Attach API,它允许一个 JVM 连接到另一个 JVM。
作用:允许一个 JVM 连接到另一个 JVM
Attach API 是在 Java 1.6 引入的。
时间:Java 1.6 之后
在 Attach API 当中,主要的类位于 com.sun.tools.attach 包,它有版本的变化:
- 在 Java 8 版本,
com.sun.tools.attach包位于JDK_HOME/lib/tools.jar文件。 - 在 Java 9 版本之后,
com.sun.tools.attach包位于jdk.attach模块(JDK_HOME/jmods/jdk.attach.jmod文件)。
位置:tools.jar 文件或 jdk.attach 模块
我们主要使用 Java 8 版本。
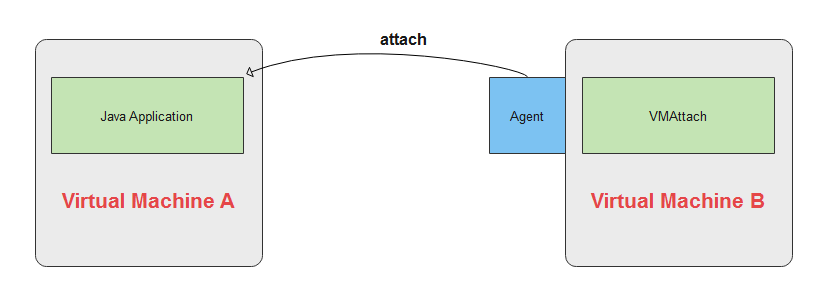
在 com.sun.tools.attach 包当中,包含的类内容如下:
com.sun.tools.attach 有哪些主要的类
┌─── spi ──────────────────────────────┼─── AttachProvider
│
├─── AgentInitializationException
│
├─── AgentLoadException
│
├─── AttachNotSupportedException
com.sun.tools.attach ───┤
├─── AttachOperationFailedException
│
├─── AttachPermission
│
├─── VirtualMachine
│
└─── VirtualMachineDescriptor
在上面这些类当中,我们忽略掉其中的 Exception 和 Permission 类,简化之后如下:
┌─── spi ────────────────────────┼─── AttachProvider
│
com.sun.tools.attach ───┼─── VirtualMachine
│
└─── VirtualMachineDescriptor
在这三个类当中,核心的类是 VirtualMachine 类,代码围绕着它来展开;
VirtualMachineDescriptor 类比较简单,就是对几个字段(id、provider 和 display name)的包装;
而 AttachProvider 类提供了底层实现。
VirtualMachine
A com.sun.tools.attach.VirtualMachine represents a Java virtual machine to which this Java virtual machine has attached.
The Java virtual machine to which it is attached is sometimes called the target virtual machine, or target VM.
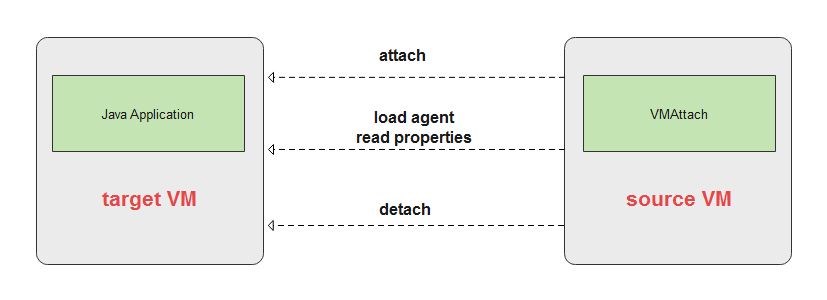
使用 VirtualMachine 类,我们分成三步:
- 第一步,与 target VM 建立连接,获得一个
VirtualMachine对象。 - 第二步,使用
VirtualMachine对象,可以将 Agent Jar 加载到 target VM 上,也可以从 target VM 读取一些属性信息。 - 第三步,与 target VM 断开连接。
┌─── VirtualMachine.attach(String id)
┌─── 1. Get VM ──────┤
│ └─── VirtualMachine.attach(VirtualMachineDescriptor vmd)
│
│ ┌─── VirtualMachine.loadAgent(String agent)
│ ┌─── Load Agent ────────┤
VirtualMachine ───┤ │ └─── VirtualMachine.loadAgent(String agent, String options)
├─── 2. Use VM ──────┤
│ │ ┌─── VirtualMachine.getAgentProperties()
│ └─── read properties ───┤
│ └─── VirtualMachine.getSystemProperties()
│
└─── 3. detach VM ───┼─── VirtualMachine.detach()
Get VM
attach 1
A VirtualMachine is obtained by invoking the attach method with an identifier that identifies the target virtual machine.
The identifier is implementation-dependent but is typically the process identifier (or pid) in environments
where each Java virtual machine runs in its own operating system process.
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public static VirtualMachine attach(String id) throws AttachNotSupportedException, IOException {
// ...
}
}
attach 2
Alternatively, a VirtualMachine instance is obtained by invoking the attach method with a VirtualMachineDescriptor
obtained from the list of virtual machine descriptors returned by the list method.
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public static VirtualMachine attach(VirtualMachineDescriptor vmd) throws AttachNotSupportedException, IOException {
// ...
}
}
Use VM
Load Agent
Once a reference to a virtual machine is obtained, the loadAgent, loadAgentLibrary, and loadAgentPath methods are used to load agents into target virtual machine.
- The
loadAgentmethod is used to load agents that are written in the Java Language and deployed in a JAR file. - The
loadAgentLibraryandloadAgentPathmethods are used to load agents that are deployed either in a dynamic library or statically linked into the VM and make use of the JVM Tools Interface.
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public void loadAgent(String agent) throws AgentLoadException, AgentInitializationException, IOException {
loadAgent(agent, null);
}
public abstract void loadAgent(String agent, String options)
throws AgentLoadException, AgentInitializationException, IOException;
}
read properties
In addition to loading agents a VirtualMachine provides read access to the system properties in the target VM.
This can be useful in some environments where properties such as java.home, os.name, or os.arch are used to
construct the path to agent that will be loaded into the target VM.
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public abstract Properties getSystemProperties() throws IOException;
public abstract Properties getAgentProperties() throws IOException;
}
这两个方法的区别:getAgentProperties() 是 VM 为 agent 专门维护的属性。
getSystemProperties(): This method returns the system properties in the target virtual machine. Properties whose key or value is not aStringare omitted. The method is approximately equivalent to the invocation of the methodSystem.getProperties()in the target virtual machine except that properties with a key or value that is not aStringare not included.getAgentProperties(): The target virtual machine can maintain a list of properties on behalf of agents. The manner in which this is done, the names of the properties, and the types of values that are allowed, is implementation specific. Agent properties are typically used to store communication end-points and other agent configuration details.
Detach VM
Detach from the virtual machine.
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public abstract void detach() throws IOException;
}
其他方法
第一个是 id() 方法,它返回 target VM 的进程 ID 值。
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
private final String id;
public final String id() {
return id;
}
}
第二个是 list() 方法,它返回一组 VirtualMachineDescriptor 对象,描述所有潜在的 target VM 对象。
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
public static List<VirtualMachineDescriptor> list() {
// ...
}
}
第三个是 provider() 方法,它返回一个 AttachProvider 对象。
public abstract class VirtualMachine {
private final AttachProvider provider;
public final AttachProvider provider() {
return provider;
}
}
VirtualMachineDescriptor
A com.sun.tools.attach.VirtualMachineDescriptor is a container class used to describe a Java virtual machine.
public class VirtualMachineDescriptor {
private String id;
private String displayName;
private AttachProvider provider;
public String id() {
return id;
}
public String displayName() {
return displayName;
}
public AttachProvider provider() {
return provider;
}
}
- an identifier that identifies a target virtual machine.
- a reference to the
AttachProviderthat should be used when attempting to attach to the virtual machine. - The display name is typically a human readable string that a tool might display to a user.
VirtualMachineDescriptor instances are typically created by invoking the VirtualMachine.list() method.
This returns the complete list of descriptors to describe the Java virtual machines known to all installed attach providers.
AttachProvider
com.sun.tools.attach.spi.AttachProvider 是一个抽象类,它需要一个具体的实现:
public abstract class AttachProvider {
//...
}
不同平台上的 JVM,它对应的具体 AttachProvider 实现是不一样的:
- Linux:
sun.tools.attach.LinuxAttachProvider - Windows:
sun.tools.attach.WindowsAttachProvider
An attach provider implementation is typically tied to a Java virtual machine implementation, version, or even mode of operation. That is, a specific provider implementation will typically only be capable of attaching to a specific Java virtual machine implementation or version. For example, Sun’s JDK implementation ships with provider implementations that can only attach to Sun’s HotSpot virtual machine.
An attach provider is identified by its name and type:
- The
nameis typically, but not required to be, a name that corresponds to the VM vendor. The Sun JDK implementation, for example, ships with attach providers that use the name “sun”. - The
typetypically corresponds to the attach mechanism. For example, an implementation that uses the Doors inter-process communication mechanism might use the type “doors”.
The purpose of the name and type is to identify providers in environments where there are multiple providers installed.
总结
本文内容总结如下:
- 第一点,Attach API 位于
com.sun.tools.attach包:- 在 Java 8 版本,
com.sun.tools.attach包位于JDK_HOME/lib/tools.jar文件。 - 在 Java 9 版本之后,
com.sun.tools.attach包位于jdk.attach模块(JDK_HOME/jmods/jdk.attach.jmod文件)。
- 在 Java 8 版本,
- 第二点,在
com.sun.tools.attach包当中,重要的类有三个:VirtualMachine(核心功能)、VirtualMachineDescriptor(三个属性)和AttachProvider(底层实现)。 - 第三点,使用
VirtualMachine类分成三步:- 第一步,与 target VM 建立连接,获得一个
VirtualMachine对象。 - 第二步,使用
VirtualMachine对象,可以将 Agent Jar 加载到 target VM 上,也可以从 target VM 读取一些属性信息。 - 第三步,与 target VM 断开连接。
- 第一步,与 target VM 建立连接,获得一个
