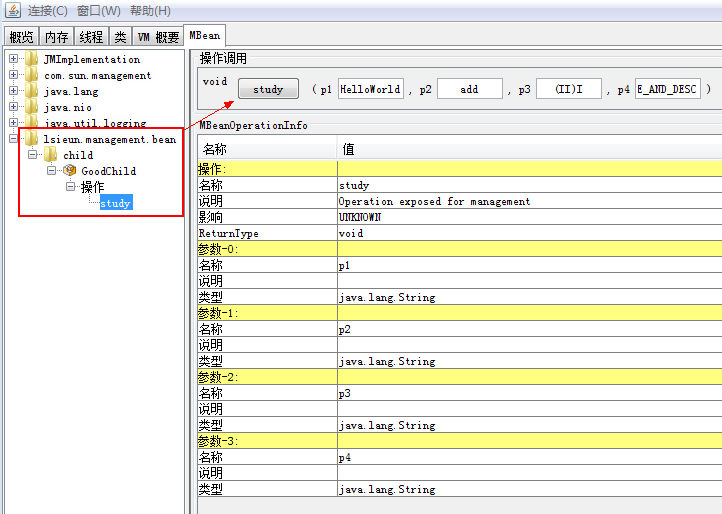
MBean
GoodChildMBean
package lsieun.management.bean;
public interface GoodChildMBean {
void study(String className, String methodName, String methodDesc, String options);
}
GoodChild
package lsieun.management.bean;
import lsieun.asm.visitor.MethodInfo;
import lsieun.cst.Const;
import lsieun.instrument.InabilityTransformer;
import java.lang.instrument.ClassFileTransformer;
import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
import java.util.Formatter;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class GoodChild implements GoodChildMBean {
protected final Instrumentation instrumentation;
public GoodChild(Instrumentation instrumentation) {
this.instrumentation = instrumentation;
}
@Override
public void study(String className, String methodName, String methodDesc, String option) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Formatter fm = new Formatter(sb);
fm.format("%s%n", Const.SEPARATOR);
fm.format("GoodChild.study%n");
fm.format(" class : %s%n", className);
fm.format(" method : %s:%s%n", methodName, methodDesc);
fm.format(" option : %s%n", option);
fm.format(" thread : %s@%s(%s)%n",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),
Thread.currentThread().getId(),
Thread.currentThread().isDaemon()
);
fm.format("%s%n", Const.SEPARATOR);
System.out.println(sb);
Set<MethodInfo> flags = new HashSet<>();
if (option != null) {
String[] array = option.split(",");
for (String element : array) {
if ("".equals(element)) continue;
MethodInfo methodInfo = Enum.valueOf(MethodInfo.class, element);
flags.add(methodInfo);
}
}
// 第一种方式,用 Class.forName()方法,速度较快
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
transform(clazz, methodName, methodDesc, flags);
return;
} catch (Exception ex) { /* Nope */ }
// 第二种方式,用 Instrumentation.getAllLoadedClasses()方法,速度较慢
Class<?>[] allLoadedClasses = instrumentation.getAllLoadedClasses();
for (Class<?> clazz : allLoadedClasses) {
if (clazz.getName().equals(className)) {
transform(clazz, methodName, methodDesc, flags);
return;
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to locate class [" + className + "]");
}
/**
* Registers a transformer and executes the transform
*
* @param clazz The class to transform
* @param methodName The method name to instrument
* @param methodDesc The method signature to match
*/
protected void transform(Class<?> clazz, String methodName, String methodDesc, Set<MethodInfo> flags) {
ClassLoader classLoader = clazz.getClassLoader();
ClassFileTransformer transformer = new InabilityTransformer(classLoader, clazz.getName(), methodName, methodDesc, flags);
instrumentation.addTransformer(transformer, true);
try {
instrumentation.retransformClasses(clazz);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to transform [" + clazz.getName() + "]", ex);
} finally {
instrumentation.removeTransformer(transformer);
}
}
}
Agent Jar
DynamicAgent
package lsieun.agent;
import lsieun.cst.Const;
import lsieun.management.bean.GoodChild;
import lsieun.utils.*;
import javax.management.MBeanServer;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
public class DynamicAgent {
public static void agentmain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation inst) throws Exception {
// 第一步,打印信息:agentArgs, inst, classloader, thread
PrintUtils.printAgentInfo(DynamicAgent.class, "Agent-Class", agentArgs, inst);
// 第二步,创建 MBean
System.out.println("Installing JMX Agent...");
GoodChild child = new GoodChild(inst);
ObjectName objectName = new ObjectName(Const.GOOD_CHILD_BEAN);
// 第三步,注册 MBean
MBeanServer beanServer = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
beanServer.registerMBean(child, objectName);
// 第四步,设置属性
System.setProperty(Const.AGENT_MANAGEMENT_PROP, "true");
System.out.println("JMX Agent Installed");
}
}
JMX Client
AgentInstaller
package run.jmx;
import com.sun.tools.attach.VirtualMachine;
import lsieun.cst.Const;
import lsieun.utils.JarUtils;
import lsieun.utils.VMAttachUtils;
import javax.management.MBeanServerConnection;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnector;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnectorFactory;
import javax.management.remote.JMXServiceURL;
import java.util.Properties;
public class AgentInstaller {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 第一步,获取 PID
String displayName = "sample.Program";
String pid = VMAttachUtils.findPID(displayName);
System.out.println("pid: " + pid);
// 第二步,利用 Attach 机制,加载两个 Agent Jar
VirtualMachine vm = VirtualMachine.attach(pid);
Properties properties = vm.getSystemProperties();
String value = properties.getProperty(Const.AGENT_MANAGEMENT_PROP);
if (value == null) {
// 加载第一个 Agent Jar
String jarPath = JarUtils.getJarPath();
vm.loadAgent(jarPath);
}
String connectorAddress = vm.getAgentProperties().getProperty(Const.LOCAL_CONNECTOR_ADDRESS_PROP, null);
vm.getAgentProperties().list(System.out);
if (connectorAddress == null) {
// 加载第二个 Agent Jar
String home = vm.getSystemProperties().getProperty("java.home");
String managementAgentJarPath = JarUtils.getManagementAgentJarPath(home);
vm.loadAgent(managementAgentJarPath);
connectorAddress = vm.getAgentProperties().getProperty(Const.LOCAL_CONNECTOR_ADDRESS_PROP, null);
vm.getAgentProperties().list(System.out);
}
System.out.println(connectorAddress);
vm.detach();
// 第三步,准备参数
String beanName = Const.GOOD_CHILD_BEAN;
String beanMethodName = "study";
String[] beanMethodArgArray = new String[]{
// "sample.HelloWorld", "add", "(II)I", "",
"sample.HelloWorld", "add", "(II)I", "NAME_AND_DESC,PARAMETER_VALUES",
// "sample.HelloWorld", "add", "(II)I", "NAME_AND_DESC,PARAMETER_VALUES,RETURN_VALUE",
};
// 第四步,借助 JMXConnector,调用 MBean 的方法
ObjectName objectName = new ObjectName(beanName);
JMXServiceURL serviceURL = new JMXServiceURL(connectorAddress);
try (JMXConnector connector = JMXConnectorFactory.connect(serviceURL)) {
MBeanServerConnection server = connector.getMBeanServerConnection();
server.invoke(objectName, beanMethodName, beanMethodArgArray,
new String[]{
String.class.getName(),
String.class.getName(),
String.class.getName(),
String.class.getName(),
});
}
}
}
从下面的输出结果当中,我们可以看到 GoodChild.study() 方法运行在不同的线程(thread):
GoodChild.study
class : sample.HelloWorld
method : add:(II)I
option : NAME_AND_DESC,PARAMETER_VALUES
thread : RMI TCP Connection(6)-192.168.200.1@20(true)
GoodChild.study
class : sample.HelloWorld
method : sub:(II)I
option : RETURN_VALUE
thread : RMI TCP Connection(4)-192.168.200.1@18(true)
GoodChild.study
class : sample.HelloWorld
method : sub:(II)I
option : NAME_AND_DESC
thread : RMI TCP Connection(3)-192.168.200.1@17(true)
JConsole
在下面的 jconsole 当中,study 方法的参数值:
p1:sample.HelloWorldp2:addp3:(II)Ip4:NAME_AND_DESC