如何生成控制流程图
整体思路
Instruction --> Block --> Box(图形) --> Graph(图形)
生成控制流程图经过三个步骤:
- 第一步,将Instruction组织成Block。在每个Block当中,包含1个或多个Instruction。
- 第二步,将Block封装成Box。Block就是单纯的Instruction的有序集合,而Box在Block的基础上添加了Rectangle图形信息。
- 第三步,将多个Box组织到一起,形成一个整体的Graph。
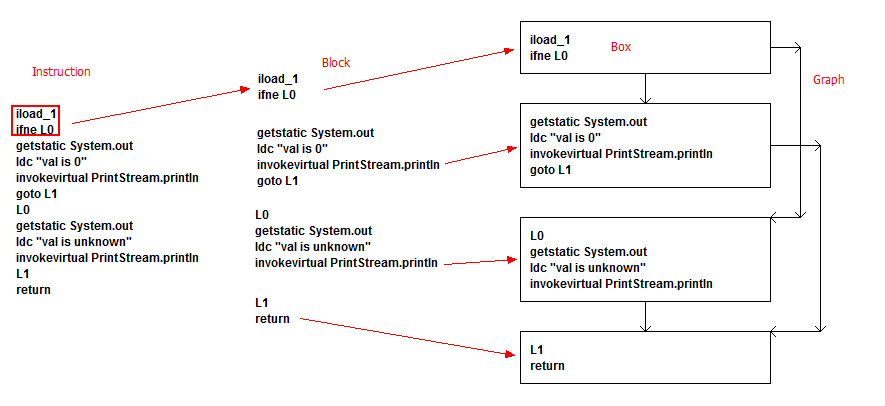
难点解析
在这个过程中,实现的难点就在于“如何将Instruction转换成Block”;其它部分,则相对容易一些。
那么,如何将Instruction转换成Block呢?我们可以依赖于Analyzer类的newControlFlowEdge方法来实现。
在Analyzer类中,newControlFlowEdge方法提供了一个空的实现:
protected void newControlFlowEdge(final int insnIndex, final int successorIndex) {
// Nothing to do.
}
如果我们仔细观察一下,就会发现:newControlFlowEdge方法是在analyze方法进行调用。
在analyze方法中,根据当前指令(insnNode)的类型,会对newControlFlowEdge方法的调用,有以下几种情况:
- 如果当前的
insnNode是LabelNode、LineNumberNode或FrameNode类型- 它们并不是真正意义上的instruction(不会存储到具体的
.class文件中),只是起到辅助作用,按照顺序执行就可以了。
- 它们并不是真正意义上的instruction(不会存储到具体的
- 如果当前的
insnNode是JumpInsnNode类型- 它代表选择结构,判断是否要进行跳转。
- 注意,
if语句有两个分支,一个是true,另一个是false;而goto就只有一个分支,不需要考虑true或false,直接跳转就可以了。
- 如果当前的
insnNode是LookupSwitchInsnNode或TableSwitchInsnNode类型- 它代表多重选择跳转,有多个分支结构。
if语句只有两个分支,而switch可以支持更多分支,支持default和多个case的情况。
- 它代表多重选择跳转,有多个分支结构。
- 如果当前的
insnNode是ATHROW或RETURN等代表结束的opcode,它表示方法的执行结束,没有任何的跳转分支。 - 其它情况(大多数的指令都是属于这种),按照顺序执行。
public class Analyzer<V extends Value> implements Opcodes {
public Frame<V>[] analyze(final String owner, final MethodNode method) throws AnalyzerException {
// Control flow analysis.
while (numInstructionsToProcess > 0) {
// Get and remove one instruction from the list of instructions to process.
int insnIndex = instructionsToProcess[--numInstructionsToProcess];
// Simulate the execution of this instruction.
AbstractInsnNode insnNode = null;
try {
insnNode = method.instructions.get(insnIndex);
int insnOpcode = insnNode.getOpcode();
int insnType = insnNode.getType();
if (insnType == AbstractInsnNode.LABEL
|| insnType == AbstractInsnNode.LINE
|| insnType == AbstractInsnNode.FRAME) {
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, insnIndex + 1); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
} else {
if (insnNode instanceof JumpInsnNode) {
JumpInsnNode jumpInsn = (JumpInsnNode) insnNode;
if (insnOpcode != GOTO && insnOpcode != JSR) {
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, insnIndex + 1); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
}
int jumpInsnIndex = insnList.indexOf(jumpInsn.label);
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, jumpInsnIndex); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
} else if (insnNode instanceof LookupSwitchInsnNode) {
LookupSwitchInsnNode lookupSwitchInsn = (LookupSwitchInsnNode) insnNode;
int targetInsnIndex = insnList.indexOf(lookupSwitchInsn.dflt);
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, targetInsnIndex); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
for (int i = 0; i < lookupSwitchInsn.labels.size(); ++i) {
LabelNode label = lookupSwitchInsn.labels.get(i);
targetInsnIndex = insnList.indexOf(label);
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, targetInsnIndex); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
}
} else if (insnNode instanceof TableSwitchInsnNode) {
TableSwitchInsnNode tableSwitchInsn = (TableSwitchInsnNode) insnNode;
int targetInsnIndex = insnList.indexOf(tableSwitchInsn.dflt);
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, targetInsnIndex); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
for (int i = 0; i < tableSwitchInsn.labels.size(); ++i) {
LabelNode label = tableSwitchInsn.labels.get(i);
targetInsnIndex = insnList.indexOf(label);
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, targetInsnIndex); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
}
} else if (insnOpcode != ATHROW && (insnOpcode < IRETURN || insnOpcode > RETURN)) {
newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, insnIndex + 1); // 这里调用了newControlFlowEdge方法
}
}
} catch (AnalyzerException e) {
throw new AnalyzerException(e.node, "Error at instruction " + insnIndex + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// DontCheck(IllegalCatch): can't be fixed, for backward compatibility.
throw new AnalyzerException(insnNode, "Error at instruction " + insnIndex + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
return frames;
}
}
图形部分
在项目当中提供了TextGraph类,可以用文本的形式将control flow graph打印出来。
┌───────────────────────────────────┐
│ iload_1 │
│ ifne L0 ├───┐
└────────────────┬──────────────────┘ │
│ │
┌────────────────┴──────────────────┐ │
│ getstatic System.out │ │
│ ldc "val is 0" │ │
│ invokevirtual PrintStream.println │ │
│ goto L1 ├───┼──┐
└───────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ │
┌───────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ L0 ├───┘ │
│ getstatic System.out │ │
│ ldc "val is unknown" │ │
│ invokevirtual PrintStream.println │ │
└────────────────┬──────────────────┘ │
│ │
┌────────────────┴──────────────────┐ │
│ L1 ├──────┘
│ return │
└───────────────────────────────────┘
图形部分的代码位于`lsieun.graphics`包内,这些代码是从Simple Java Graphics网站复制而来的。
https://horstmann.com/sjsu/graphics/
那么,为什么使用这些代码呢?一方面,是简单且容易使用;另一方面,不会引入额外的jar包依赖,因此我们的关注点集中在ASM相关的jar包上。
代码实现
接下来,我们要将抽象思路转换成具体的代码实现。

| 概念 | 类 |
|---|---|
| instruction | AbstractInsnNode |
| block | InsnBlock |
| box | InsnBox |
| graph | InsnGraph |
InsnBlock
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class InsnBlock {
// 文字信息
public final List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();
// 关联关系
public final List<InsnBlock> nextBlockList = new ArrayList<>();
public final List<InsnBlock> jumpBlockList = new ArrayList<>();
public void addLines(List<String> list) {
lines.addAll(list);
}
public void addNext(InsnBlock item) {
nextBlockList.add(item);
}
public void addJump(InsnBlock item) {
jumpBlockList.add(item);
}
}
InsnBox
import lsieun.graphics.Rectangle;
import lsieun.graphics.Text;
public class InsnBox {
private static final int INNER_PADDING = 10;
private static final int RECTANGLE_WIDTH = 250;
// 位置信息
public int x;
public int y;
// 图形信息
public Rectangle rectangle;
public final InsnBlock block;
public InsnBox(InsnBlock block) {
this.block = block;
}
public void draw(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
int currentX = x + INNER_PADDING;
int currentY = y + INNER_PADDING;
int currentWidth = 0;
int currentHeight = 0;
for (String item : block.lines) {
Text text = new Text(currentX, currentY, item);
text.draw();
int textWidth = text.getWidth() + 2 * INNER_PADDING;
if (textWidth > currentWidth) {
currentWidth = textWidth;
}
currentY += text.getHeight();
currentHeight = currentY - y;
}
int width = RECTANGLE_WIDTH;
int height = currentHeight + INNER_PADDING;
rectangle = new Rectangle(x, y, width, height);
rectangle.draw();
}
public int getWidth() {
if (rectangle != null) {
return rectangle.getWidth();
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
public int getHeight() {
if (rectangle != null) {
return rectangle.getHeight();
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}
InsnGraph

public class InsnGraph {
// 部分内容省略
private static final int START_X = 10;
private static final int START_Y = 10;
private final int startX;
private final int startY;
private final InsnBox[] boxes;
public InsnGraph(InsnBlock[] blocks) {
this(START_X, START_Y, blocks);
}
public InsnGraph(int startX, int startY, InsnBlock[] blocks) {
this.startX = startX;
this.startY = startY;
int length = blocks.length;
this.boxes = new InsnBox[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
this.boxes[i] = new InsnBox(blocks[i]);
}
}
public void draw() {
int length = boxes.length;
if (length < 1) return;
drawBlockRectangles();
drawConnectionLines();
}
private void drawBlockRectangles() {
int currentX = this.startX;
int currentY = this.startY;
int length = boxes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
InsnBox box = boxes[i];
if (i != 0) {
InsnBox previousBox = boxes[i - 1];
currentY = previousBox.y + previousBox.getHeight() + ROW_SPACE;
}
box.draw(currentX, currentY);
}
}
private void drawConnectionLines() {
int length = boxes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
InsnBox currentBox = boxes[i];
List<InsnBox> nextBoxList = findNextBoxes(currentBox);
for (InsnBox nextBox : nextBoxList) {
connectTop2BottomBlock(currentBox.rectangle, nextBox.rectangle);
}
List<InsnBox> jumpBoxList = findJumpBoxes(currentBox);
for (InsnBox jumpbox : jumpBoxList) {
jumpOne2Another(currentBox.rectangle, jumpbox.rectangle, i);
}
}
}
// 后续内容省略
}
第一个版本
首先,我们先做一个简单的实现:每个Instruction生成一个Block。
import lsieun.asm.analysis.graph.InsnBlock;
import org.objectweb.asm.tree.AbstractInsnNode;
import org.objectweb.asm.tree.MethodNode;
import org.objectweb.asm.tree.analysis.*;
import java.util.List;
public class ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer<V extends Value> extends Analyzer<V> {
private AbstractInsnNode[] nodeArray;
public InsnBlock[] blocks;
public ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer(Interpreter<V> interpreter) {
super(interpreter);
}
@Override
public Frame<V>[] analyze(String owner, MethodNode method) throws AnalyzerException {
nodeArray = method.instructions.toArray();
int length = nodeArray.length;
blocks = new InsnBlock[length];
InsnText insnText = new InsnText();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
blocks[i] = getBlock(i);
AbstractInsnNode node = nodeArray[i];
List<String> lines = insnText.toLines(node);
blocks[i].addLines(lines);
}
return super.analyze(owner, method);
}
@Override
protected void newControlFlowEdge(int insnIndex, int successorIndex) {
// 首先,处理自己的代码逻辑
AbstractInsnNode insnNode = nodeArray[insnIndex];
int insnOpcode = insnNode.getOpcode();
int insnType = insnNode.getType();
if (insnType == AbstractInsnNode.JUMP_INSN) {
if ((insnIndex + 1) == successorIndex) {
addNext(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
else {
addJump(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
}
else if (insnOpcode == LOOKUPSWITCH) {
addJump(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
else if (insnOpcode == TABLESWITCH) {
addJump(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
else if (insnOpcode == RET) {
addJump(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
else if (insnOpcode == ATHROW || (insnOpcode >= IRETURN && insnOpcode <= RETURN)) {
assert false : "should not be here";
removeNextAndJump(insnIndex);
}
else {
addNext(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
// 其次,调用父类的方法实现
super.newControlFlowEdge(insnIndex, successorIndex);
}
private void addNext(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
InsnBlock currentBlock = getBlock(fromIndex);
InsnBlock nextBlock = getBlock(toIndex);
currentBlock.addNext(nextBlock);
}
private void addJump(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
InsnBlock currentBlock = getBlock(fromIndex);
InsnBlock nextBlock = getBlock(toIndex);
currentBlock.addJump(nextBlock);
}
private void removeNextAndJump(int insnIndex) {
InsnBlock currentBlock = getBlock(insnIndex);
currentBlock.nextBlockList.clear();
currentBlock.jumpBlockList.clear();
}
private InsnBlock getBlock(int insnIndex) {
InsnBlock block = blocks[insnIndex];
if (block == null){
block = new InsnBlock();
blocks[insnIndex] = block;
}
return block;
}
public InsnBlock[] getBlocks() {
return blocks;
}
}
第二个版本
接着,我们在ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer实现的基础上进一步扩展:将顺序执行多个Block合并为一个Block。
import lsieun.asm.analysis.graph.InsnBlock;
import org.objectweb.asm.tree.analysis.Interpreter;
import org.objectweb.asm.tree.analysis.Value;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer2<V extends Value> extends ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer<V> {
public ControlFlowEdgeAnalyzer2(Interpreter<V> interpreter) {
super(interpreter);
}
@Override
public InsnBlock[] getBlocks() {
//(1)调用父类实现
InsnBlock[] blocks = super.getBlocks();
//(2)如果结果为空,则提前返回
if (blocks == null || blocks.length < 1) {
return blocks;
}
//(3)记录“分隔点”
Set<InsnBlock> newBlockSet = new HashSet<>();
int length = blocks.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
InsnBlock currentBlock = blocks[i];
List<InsnBlock> nextBlockList = currentBlock.nextBlockList;
List<InsnBlock> jumpBlockList = currentBlock.jumpBlockList;
boolean hasNext = false;
boolean hasJump = false;
if (nextBlockList.size() > 0) {
hasNext = true;
}
if (jumpBlockList.size() > 0) {
hasJump = true;
}
if (!hasNext && (i + 1) < length) {
newBlockSet.add(blocks[i + 1]);
}
if (hasJump) {
newBlockSet.addAll(jumpBlockList);
if (hasNext) {
newBlockSet.add(blocks[i + 1]);
}
}
}
//(4)利用“分隔点”,合并成不同的分组
List<InsnBlock> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
InsnBlock currentBlock = blocks[i];
if (i == 0) {
resultList.add(currentBlock);
}
else if (newBlockSet.contains(currentBlock)) {
resultList.add(currentBlock);
}
else {
int size = resultList.size();
InsnBlock lastBlock = resultList.get(size - 1);
lastBlock.lines.addAll(currentBlock.lines);
lastBlock.jumpBlockList.clear();
lastBlock.jumpBlockList.addAll(currentBlock.jumpBlockList);
lastBlock.nextBlockList.clear();
lastBlock.nextBlockList.addAll(currentBlock.nextBlockList);
}
}
return resultList.toArray(new InsnBlock[0]);
}
}
验证结果
public class ControlFlowGraphRun {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";
String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);
byte[] bytes = FileUtils.readBytes(filepath);
//(1)构建ClassReader
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes);
//(2)生成ClassNode
ClassNode cn = new ClassNode();
int parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;
cr.accept(cn, parsingOptions);
//(3)查找方法
String methodName = "test";
MethodNode targetNode = null;
for (MethodNode mn : cn.methods) {
if (mn.name.equals(methodName)) {
targetNode = mn;
break;
}
}
if (targetNode == null) {
System.out.println("Can not find method: " + methodName);
return;
}
//(4)进行图形化显示
display(cn.name, targetNode, 2);
//(5)打印复杂度
CyclomaticComplexity cc = new CyclomaticComplexity();
int complexity = cc.getCyclomaticComplexity(cn.name, targetNode);
String line = String.format("%s:%s complexity: %d", targetNode.name, targetNode.desc, complexity);
System.out.println(line);
}
}
测试数据
simple
顺序执行:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
System.out.println("Hello ASM");
}
}
if
选择判断:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int val) {
if (val == 0) {
System.out.println("val is 0");
}
else {
System.out.println("val is unknown");
}
}
}
switch
多重选择:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int val) {
switch (val) {
case 0:
System.out.println("val is 0");
break;
default:
System.out.println("val is unknown");
}
}
}
for
循环语句:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
while-break
循环语句:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
int i = 1;
while (i < 10) {
if (i == 5) {
break;
}
i++;
}
}
}
throw
异常退出:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int val) {
if (val == 0) {
System.out.println("val is 0");
}
else {
throw new RuntimeException("val is unknown");
}
}
}
try-catch
异常处理:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
dead code
在之前的Tree Based Class Transformation示例当中,有一个示例是“优化跳转”,经过优化之后,有一些instruction就成为dead code。
我们可以查看内容三次变化:
- 第一次,优化之前,instruction当中存在多次跳转。
- 第二次,优化之后,减少跳转次数,出现dead code。
- 第三次,移除dead code之后,instruction精简。
总结
本文内容总结如下:
- 第一点,介绍生成control flow graph的思路:instruction –> block –> box –> graph。
- 第二点,在具体代码实现上,主要是依赖于
Analyzer类的newControlFlowEdge方法。- 第一个版本中,每一条instruction都生成一个block。
- 第二个版本中,将多个顺序执行的block合并成一个新的block。
