Stream
优化之前:
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list) {
// ''stream().forEach()'' can be replaced with 'forEach()'' (may change semantics)
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
优化之后:
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list) {
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
判断逻辑:
void visitMethodCall(Call call) {
Method m = call.resolve();
if(m.equals(STREAM_FOR_EACH) {
Expression qualifier = call.getQualifier();
if(qualifier instanceof Call) {
Method m1 = ((Call)qualifier).resolve();
if(m1.equals(COLLECTION_STREAM) {
reportWarning(call, "stream().forEach() can be replaced with forEach()");
}
}
}
}
Constant conditions & exceptions warning
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(String s, Object obj) {
if (s == null) {
// Method invocation 'trim' will produce 'NullPointerException'
System.out.println(s.trim());
}
if (s.length() == 2) {
// The call to 'substring' always fails as index is out of bounds
System.out.println(s.substring(3));
}
if (obj instanceof Number) {
// Casting 'obj' to 'String' will produce 'ClassCastException' for any non-null value
System.out.println(((String) obj).isEmpty());
}
// Condition 's.equals("no")' is always 'false'
// 因为如果s的值为no,那么它的length就应该是2。
if (s.equals("no")) {
System.out.println("Impossible!");
}
}
}
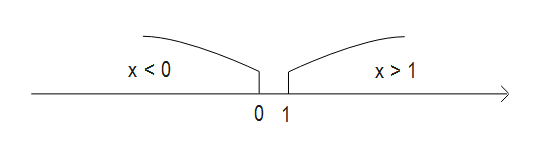
Condition is always true/false
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x) {
if (x < 0) {
if (x > 1) {
// Condition 'x > 1' is always 'false'
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int idx) {
if (Character.isLowerCase("Java".charAt(idx)) || idx < 4) {
// Condition 'Character.isLowerCase("Java".charAt(idx)) || idx < 4' is always 'true'
System.out.println(idx);
}
}
}
String.charAt(int idx):idx >= this.length-> fail;idx < 0-> fail
- 第一种情况,如果
idx == 0,那么false || true。 - 第二种情况,如果
idx == 1,那么true || true。 - 第三种情况,如果
idx == 2,那么true || true。 - 第四种情况,如果
idx == 3,那么true || true。 - 第五种情况,如果
idx > 3,那么StringIndexOutOfBoundsException || true。 - 第六种情况,如果
idx < 0,那么StringIndexOutOfBoundsException || true。
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
if (5 > 5) {
// Condition '5 > 5' is always 'false'
}
}
}
┌──────────────┐
│ if statement │
└──────────────┘
╱ ╲
┌───┐ ┌─────────┐
│ > │ │ if body │
└───┘ └─────────┘
╱ ╲ │
┌───┐ ┌───┐ ┌─────┐
│ 5 │ │ 5 │ │ ... │
└───┘ └───┘ └─────┘
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
if (12 * 3 - 19 / 6 % 4 * Math.abs(-3) > 2) {
// Condition '12 * 3 - 19 / 6 % 4 * Math.abs(-3) > 2' is always 'true'
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
if (x % 5 > y % 10 + 20) {
// Condition 'x % 5 > y % 10 + 20' is always 'false'
}
}
}
x % 5=[-4,4]y % 10 + 20=[-9, 9] + 20=[11, 29]
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
if (x * 2 == y * 4 + 1) {
// Condition 'x * 2 == y * 4 + 1' is always 'false'
}
}
}
x * 2= even(偶数)-
y * 4 + 1= odd(奇数) - 选择
x * 2,按下Ctrl + Shift + P(Expression type),显示int类型,按下Ctrl + Shift + Ptwice (Advanced expression type),显示Type: int, Range:even。 - 选择
y * 4 + 1,按下Ctrl + Shift + P(Expression type),显示int类型,按下Ctrl + Shift + Ptwice (Advanced expression type),显示Type: int, Range:<1> mod 4。
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
int x = 3;
int y = x * x; // 9
int z = x * 2; // 6
if (x + z > y) { // 3 + 6 > 9
// Condition 'x + z > y' is always 'false'
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e, int f, int g, int h) {
if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("a > 0");
}
// a>0; a<=0
if (b > 0) {
System.out.println("b > 0");
}
// a>0, b>0; a>0, b<=0; a<=0, b>0; a<=0, b<=0
if (c > 0) {
System.out.println("c > 0");
}
// 8 states
if (d > 0) {
System.out.println("d > 0");
}
// 16 states
if (e > 0) {
System.out.println("e > 0");
}
// 32 states
if (f > 0) {
System.out.println("f > 0");
}
// 64 states
if (g > 0) {
System.out.println("g > 0");
}
// 128 states
if (h > 0) {
System.out.println("h > 0");
}
// 256 states
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
int a = x > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int b = y > 0 ? 1 : 0;
if (a + b == 2) {
if (x < 0) {
// Condition 'x < 0' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
int a = x > 0 ? 1 : 0;
// State#1: x > 0, a = 1
// State#2: x <= 0, a = 0
int b = y > 0 ? 1 : 0;
// State#1: x > 0, a = 1, y > 0, b = 1
// State#2: x > 0, a = 1, y <= 0, b = 0
// State#3: x <= 0, a = 0, y > 0, b = 1
// State#4: x <= 0, a = 0, y <= 0, b = 0
if (a + b == 2) {
// State#1: x > 0, a = 1, y > 0, b = 1
if (x < 0) {
// Condition 'x < 0' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
public void test(int x, int y) {
int a = x > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int b = y > 0 ? 1 : 0;
if (a + b == 1) {
if (x == y) {
// Condition 'x == y' is always 'false'
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
int a = x > 0 ? 1 : 0;
// State#1: x > 0, a = 1
// State#2: x <= 0, a = 0
int b = y > 0 ? 1 : 0;
// State#1: x > 0, a = 1, y > 0, b = 1
// State#2: x > 0, a = 1, y <= 0, b = 0
// State#3: x <= 0, a = 0, y > 0, b = 1
// State#4: x <= 0, a = 0, y <= 0, b = 0
if (a + b == 1) {
// State#2: x > 0, a = 1, y <= 0, b = 0
// State#3: x <= 0, a = 0, y > 0, b = 1
if (x == y) {
// Condition 'x == y' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
Type constrains
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Number) return;
// State: obj not instanceof Number
if (obj instanceof CharSequence) return;
// State not instanceof Number, CharSequence
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
// Condition 'obj instanceof Integer' is always 'false'
System.out.println("Impossible");
}
if (obj instanceof StringBuilder) {
// Condition 'obj instanceof StringBuilder' is always 'false'
System.out.println("Also impossible");
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
static class A {
}
static class B extends A {
}
public void test(A a1) {
// a1 instanceof A
B b1 = (B) a1;
A a2 = new A();
// a2 exactly A
// Casting 'a2' to 'B' will produce 'ClassCastException' for any non-null value
B b2 = (B) a2;
}
}
Nullness
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(String s) {
if (s == null) {
System.out.println("String is null!");
}
System.out.println(s.trim());
}
}
public void test(String s) {
// 没有提示
System.out.println(s.trim());
}
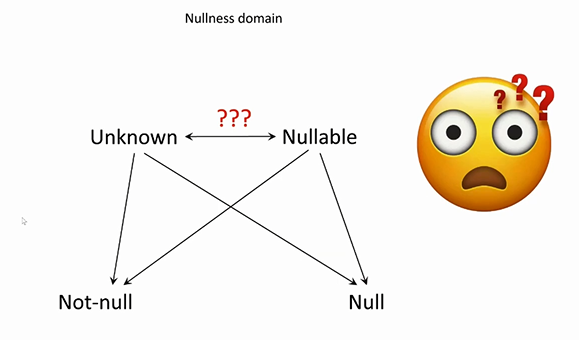
Nullness kinds:
- not-null
- unknown
- nullable
- null
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(String s) {
// State: s:nullness = unknown
if (s == null) {
// State: s:nullness = null
System.out.println("String is null!");
}
// State#1: s:nullness = not-null
// State#2: s:nullness = null
// Merged state: s:nullness = nullable
// Method invocation 'trim' may produce 'NullPointerException'
System.out.println(s.trim());
}
}
Tracking relations
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(Object a, Object b, Object c) {
if (a == b && b == c) {
if (a != c) {
// Condition 'a != c' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(String a, String b, String c) {
if (a.equals(b) && b.equals(c)) {
if (!a.equals(c)) {
// Condition '!a.equals(c)' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y, int z) {
if (x < y) return;
if (y < z) return;
if (x < z) {
// Condition 'x < z' is always 'false'
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
if (x == y) return;
int diff = x - y;
if (diff == 0) {
// Condition 'diff == 0' is always 'false'
}
}
}
Field
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
}
public void test(Point p) {
p.x = 10;
p.y = 10;
// System.out.println("Hello!");
if (p.x == p.y) { // Condition 'p.x == p.y' is always 'true'
System.out.println("Impossible");
}
}
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class HelloWorld {
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
}
public static void test(Point p) {
p.x = 10;
p.y = 10;
System.out.println("Hello!");
if (p.x == p.y) { // Not always false anymore?
System.out.println("Impossible");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point();
System.setOut(new PrintStream(System.out) {
@Override
public void println(String x) {
super.println(x);
p.x = p.y = 0;
}
});
test(p);
}
}
Pure methods
public class HelloWorld {
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
}
public static void test(Point p) {
p.x = 10;
p.y = 20;
double z = Math.sqrt(2);
if (p.x == p.y) { // Condition 'p.x == p.y' is always 'false'
System.out.println("Impossible");
}
}
}
Locality tracking
public class HelloWorld {
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
}
public static void test() {
Point p = new Point();
p.x = 10;
p.y = 20;
System.out.println("Hello!");
if (p.x == p.y) { // Condition 'p.x == p.y' is always 'false'
System.out.println("Impossible");
}
}
}
Array elements
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(int[] array) {
if (array[0] == array[1]) {
// Result of 'array[0] - array[1]' is always '0'
int diff = array[0] - array[1];
System.out.println(diff);
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(int[] array, int i) {
if (array[0] == array[1]) {
array[i] = 10;
int diff = array[0] - array[1];
System.out.println(diff);
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(int[] array, int i) {
if (array[0] == array[1] && i >= 2) {
array[i] = 10;
int diff = array[0] - array[1];
System.out.println(diff);
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(int[] array, int i, int j) {
if (array[i] == array[j]) {
int diff = array[i] - array[j];
System.out.println(diff);
}
}
}
Getters
public class HelloWorld {
public final class Point {
private final int x;
private final int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
}
public static void test(Point p) {
if (p.getX() % 2 == 1) {
if (p.getX() == p.getY() * 2) {
// Condition 'p.getX() == p.getY() * 2' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
Special fields
- Array length
- String length
- Collection size(mutable)
- Map size(mutable)
- Optional value
- Boxed value
Hardcoded contracts
String.isEmpty(): this.length == 0 -> true; else -> false
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(String s) {
if (s.isEmpty()) return;
int length = s.length();
if (length >= 1) {
// Condition 'length >= 1' is always 'true'
}
}
}
String.startsWith(String str):this.length < str.length-> false
public class HelloWorld {
public static void test(String s) {
if (s.startsWith("--")) {
if (s.isEmpty()) {
// Condition 's.isEmpty()' is always 'false'
}
}
}
}
Method handlers
Method ranges
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(LocalDate date) {
int day = date.getDayOfMonth();
if (day == 0) {
// Condition 'day == 0' is always 'false'
}
}
}
Mutability
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> input) {
List<String> list = Collections.unmodifiableList(input);
list.add("Java"); // Immutable object is modified
}
}
Common dataflow
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int x, int y) {
if (x == y) {
// Division by zero
System.out.println(1 / (x - y));
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list) {
if (!list.isEmpty()) return;
// Collection 'list' is always empty
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public long test(int hour, int minutes, int seconds) {
// hour * 3600: integer multiplication implicitly cast to long
return hour * 3600 + minutes * 60 + seconds;
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public long test(int hour, int minutes, int seconds) {
assert hour >= 0 && hour < 24;
assert minutes >= 0 && minutes < 60;
assert seconds >= 0 && seconds < 60;
return hour * 3600 + minutes * 60 + seconds;
}
}
在return语句中,选中hour * 3600 + minutes * 60 + seconds部分,按下两次Ctrl + Shift + P,可以查看这个表达式的Range。
Dataflow in quick-fixes
优化之前:
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list, int maxSize) {
// Can be replaced with 'List.subList().clear()'
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i > maxSize; i--) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
}
优化之后:
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list, int maxSize) {
if (list.size() > maxSize + 1) {
list.subList(maxSize + 1, list.size()).clear();
}
}
}
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list, int maxSize) {
if (maxSize >= list.size()) return;
// Can be replaced with 'List.subList().clear()'
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i > maxSize; i--) {
list.remove(i);
}
}
}
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(List<String> list, int maxSize) {
if (maxSize >= list.size()) return;
if (list.size() > maxSize + 1) {
list.subList(maxSize + 1, list.size()).clear();
}
}
}
考虑是否能做到
public class HelloWorld {
public int val;
public int getVal() {
return val;
}
public void test() {
this.val = getVal(); // 取自己的值,然后赋值给自己。
}
}
Conclusion
- Data flow analysis performs abstract interpretation of your code
- It tracks constant values, ranges, oddity, types, nullability, mutability, variable equality and so on
- It knows about behavior of many library methods
- See how data flow analysis works using advanced expression type feature (
Ctrl + Shift + Pseveral times) - Data flow analysis is everywhere: inspections, quick-fixes, completions, debugger, advanced expression type, refactorings, “dataflow to here”.
