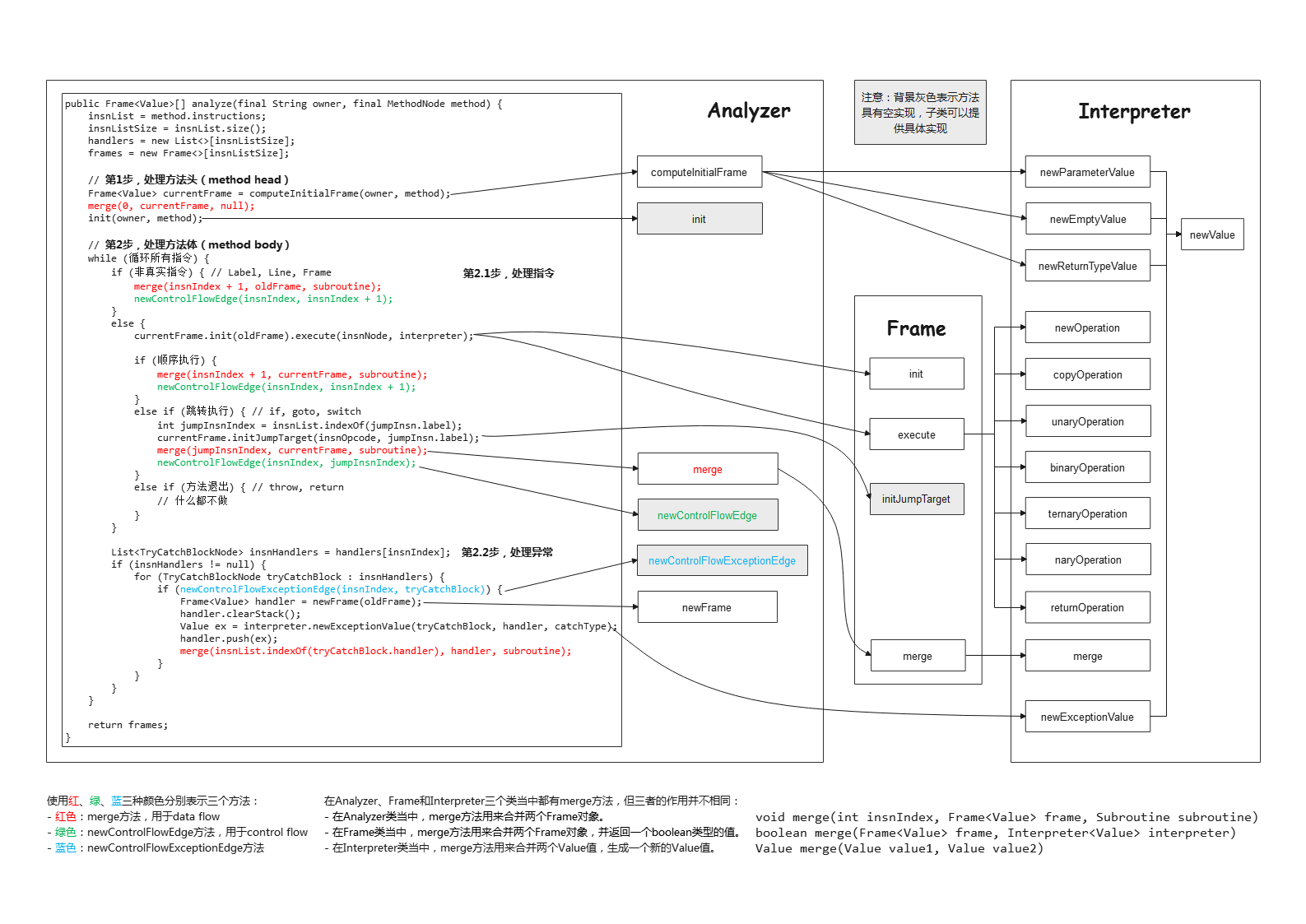
在本文当中,我们介绍Frame、Interpreter和Value三个类。
Frame类
从源码的角度来讲,Frame是一个泛型类,它的定义如下:
public class Frame<V extends Value> {
//...
}
为了方便理解,我们可以暂时忽略掉它的泛型信息。也就是说,我们将泛型V直接替换成Value类型。
class info
第一个部分,Frame类继承自Object类。
public class Frame {
}
fields
第二个部分,Frame类定义的字段有哪些。其中,
returnValue和values字段分别对应于方法的“返回值”和“方法参数”。- 其实,
values字段,除了包含“方法参数”,它更确切的可以理解为local variable和operand stack拼接之后的结果。
- 其实,
numLocals字段表示local variable的大小,而numStack字段当前operand stack上有多少个元素。
public class Frame {
private Value returnValue;
private Value[] values;
private int numLocals;
private int numStack;
}
constructors
第三个部分,Frame类定义的构造方法有哪些。在Frame当中,一共定义了两个构造方法。
先来看第一个构造方法,用来创建一个全新的Frame对象:
- 方法参数:
int numLocals和int numStack分别表示local variable和operand stack的大小。 - 方法体:
- 初始化
values数组的大小。 - 记录
numLocals字段的值。 - 另外,注意没有给
numStack赋值,其初始值则为0,表示在刚进入方法的时候,operand stack上没有任何元素。
- 初始化
public class Frame {
public Frame(int numLocals, int numStack) {
this.values = new Value[numLocals + numStack];
this.numLocals = numLocals;
// 注意,这里并没有对numStack字段进行赋值。
}
}
第二个构造方法,是对已有的frame进行复制:
- 方法参数:接收一个
Frame类型的参数 - 方法体:
- 调用
this(int,int)构造方法,来初始化values字段和numLocals字段。 - 调用
init(Frame)方法,为values数组中元素赋值,并为numStack字段赋值。
- 调用
public class Frame {
public Frame(Frame frame) {
this(frame.numLocals, frame.values.length - frame.numLocals);
init(frame);
}
public Frame init(Frame frame) {
returnValue = frame.returnValue;
System.arraycopy(frame.values, 0, values, 0, values.length);
numStack = frame.numStack;
return this;
}
}
methods
第四个部分,Frame类定义的方法有哪些。
locals相关方法
下面这些方法是与local variable相关的方法:
getLocals()方法:获取local variable的大小getLocal(int)方法:获取local variable当中某一个元素的值。setLocal(int, Value)方法:给local variable当中的某一个元素进行赋值。
public class Frame {
public int getLocals() {
return numLocals;
}
public Value getLocal(int index) {
if (index >= numLocals) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Trying to get an inexistant local variable " + index);
}
return values[index];
}
public void setLocal(int index, Value value) {
if (index >= numLocals) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Trying to set an inexistant local variable " + index);
}
values[index] = value;
}
}
stack相关方法
下面这些方法是与operand stack相关的方法:
getMaxStackSize()方法:获取operand stack的总大小。getStackSize()方法:获取operand stack的当前大小。clearStack()方法:将operand stack的当前大小设置为0值。getStack(int)方法:获取operand stack的某一个元素。setStack(int, Value)方法:设置operand stack的某一个元素。pop()方法:将operand stack最上面的元素进行出栈。push(Value)方法:将某一个元素压进operand stack当中。
public class Frame {
public int getMaxStackSize() {
return values.length - numLocals;
}
public int getStackSize() {
return numStack;
}
public void clearStack() {
numStack = 0;
}
public Value getStack(int index) {
return values[numLocals + index];
}
public void setStack(int index, Value value) {
values[numLocals + index] = value;
}
public Value pop() {
if (numStack == 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Cannot pop operand off an empty stack.");
}
return values[numLocals + (--numStack)];
}
public void push(Value value) {
if (numLocals + numStack >= values.length) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Insufficient maximum stack size.");
}
values[numLocals + (numStack++)] = value;
}
}
init方法
init方法用来将另一个Frame里的值复制到当前Frame当中。
public class Frame {
public Frame init(final Frame frame) {
returnValue = frame.returnValue;
System.arraycopy(frame.values, 0, values, 0, values.length);
numStack = frame.numStack;
return this;
}
}
execute方法
下面的execute(AbstractInsnNode, Interpreter)方法,是模拟某一条instruction对local variable和operand stack的影响。针对某一个具体的instruction,它具体有什么样的操作,可以参考Chapter 6. The Java Virtual Machine Instruction Set。
同时,我们也要注意到execute方法也会用到Interpreter类,那么Interpreter类起到一个什么样的作用呢?Interpreter类,就是使用当前的指令(insn)和相关参数(value1、value2、value3、value4)计算出一个新的值。
public class Frame {
public void execute(AbstractInsnNode insn, Interpreter interpreter) throws AnalyzerException {
Value value1;
Value value2;
Value value3;
Value value4;
int var;
switch (insn.getOpcode()) {
case Opcodes.NOP:
break;
case Opcodes.ACONST_NULL:
case Opcodes.ICONST_M1:
case Opcodes.ICONST_0:
case Opcodes.ICONST_1:
case Opcodes.ICONST_2:
case Opcodes.ICONST_3:
case Opcodes.ICONST_4:
case Opcodes.ICONST_5:
case Opcodes.LCONST_0:
case Opcodes.LCONST_1:
case Opcodes.FCONST_0:
case Opcodes.FCONST_1:
case Opcodes.FCONST_2:
case Opcodes.DCONST_0:
case Opcodes.DCONST_1:
case Opcodes.BIPUSH:
case Opcodes.SIPUSH:
case Opcodes.LDC:
// operand stack入栈:1
// 首先,由Interpreter解析出一个Value值
// 其次,将该Value值入栈到operand stack上
push(interpreter.newOperation(insn));
break;
case Opcodes.ILOAD:
case Opcodes.LLOAD:
case Opcodes.FLOAD:
case Opcodes.DLOAD:
case Opcodes.ALOAD:
// operand stack入栈:1
// 首先,从local variable当中取出一个Value值
// 其次,由Interpreter将旧的Value值解析成一个新的Value值
// 最后,将新Value值入栈到operand stack上
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, getLocal(((VarInsnNode) insn).var)));
break;
case Opcodes.ISTORE:
case Opcodes.LSTORE:
case Opcodes.FSTORE:
case Opcodes.DSTORE:
case Opcodes.ASTORE:
// operand stack出栈:1
// 首先,从operand stack当中出栈一个Value值
// 其次,由Interpreter将旧的Value值解析成一个新的Value值
// 最后,将新Value值存储到local variable上
value1 = interpreter.copyOperation(insn, pop());
var = ((VarInsnNode) insn).var;
setLocal(var, value1);
if (value1.getSize() == 2) {
setLocal(var + 1, interpreter.newEmptyValue(var + 1));
}
if (var > 0) {
Value local = getLocal(var - 1);
if (local != null && local.getSize() == 2) {
setLocal(var - 1, interpreter.newEmptyValue(var - 1));
}
}
break;
case Opcodes.IASTORE:
case Opcodes.LASTORE:
case Opcodes.FASTORE:
case Opcodes.DASTORE:
case Opcodes.AASTORE:
case Opcodes.BASTORE:
case Opcodes.CASTORE:
case Opcodes.SASTORE:
// operand stack出栈:3
// 首先,从operand stack当中出栈三个Value值
// 其次,由Interpreter将三个旧的Value值解析成一个新的Value值
// 最后,扔掉这个新生成的Value值,因为用不到它
value3 = pop();
value2 = pop();
value1 = pop();
interpreter.ternaryOperation(insn, value1, value2, value3);
break;
case Opcodes.POP:
// operand stack出栈:1
// 首先,从operand stack当中出栈一个Value值
// 其次,扔掉这个Value值,因为用不到它
if (pop().getSize() == 2) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of POP");
}
break;
case Opcodes.POP2:
// operand stack出栈:1
// 首先,从operand stack当中出栈一个Value值
// 其次,扔掉这个Value值,因为用不到它
if (pop().getSize() == 1 && pop().getSize() != 1) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of POP2");
}
break;
case Opcodes.DUP:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:2
// 首先,从operand stack当中出栈一个Value值
// 其次,将该Value值再入栈到operand stack上
// 接着,由Interpreter将旧的Value值解析成一个新的Value值
// 最后,将这个新的Value值入栈到operand stack上
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() != 1) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP");
}
push(value1);
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
break;
case Opcodes.DUP_X1:
// operand stack出栈:2,入栈:3
value1 = pop();
value2 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() != 1 || value2.getSize() != 1) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP_X1");
}
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
push(value2);
push(value1);
break;
case Opcodes.DUP_X2:
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() == 1 && executeDupX2(insn, value1, interpreter)) {
break;
}
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP_X2");
case Opcodes.DUP2:
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() == 1) {
value2 = pop();
if (value2.getSize() == 1) {
push(value2);
push(value1);
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value2));
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
break;
}
} else {
push(value1);
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
break;
}
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP2");
case Opcodes.DUP2_X1:
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() == 1) {
value2 = pop();
if (value2.getSize() == 1) {
value3 = pop();
if (value3.getSize() == 1) {
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value2));
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
push(value3);
push(value2);
push(value1);
break;
}
}
} else {
value2 = pop();
if (value2.getSize() == 1) {
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
push(value2);
push(value1);
break;
}
}
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP2_X1");
case Opcodes.DUP2_X2:
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() == 1) {
value2 = pop();
if (value2.getSize() == 1) {
value3 = pop();
if (value3.getSize() == 1) {
value4 = pop();
if (value4.getSize() == 1) {
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value2));
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
push(value4);
push(value3);
push(value2);
push(value1);
break;
}
} else {
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value2));
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
push(value3);
push(value2);
push(value1);
break;
}
}
} else if (executeDupX2(insn, value1, interpreter)) {
break;
}
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of DUP2_X2");
case Opcodes.SWAP:
// operand stack出栈:2,入栈:2
value2 = pop();
value1 = pop();
if (value1.getSize() != 1 || value2.getSize() != 1) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal use of SWAP");
}
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value2));
push(interpreter.copyOperation(insn, value1));
break;
case Opcodes.IALOAD:
case Opcodes.LALOAD:
case Opcodes.FALOAD:
case Opcodes.DALOAD:
case Opcodes.AALOAD:
case Opcodes.BALOAD:
case Opcodes.CALOAD:
case Opcodes.SALOAD:
case Opcodes.IADD:
case Opcodes.LADD:
case Opcodes.FADD:
case Opcodes.DADD:
case Opcodes.ISUB:
case Opcodes.LSUB:
case Opcodes.FSUB:
case Opcodes.DSUB:
case Opcodes.IMUL:
case Opcodes.LMUL:
case Opcodes.FMUL:
case Opcodes.DMUL:
case Opcodes.IDIV:
case Opcodes.LDIV:
case Opcodes.FDIV:
case Opcodes.DDIV:
case Opcodes.IREM:
case Opcodes.LREM:
case Opcodes.FREM:
case Opcodes.DREM:
case Opcodes.ISHL:
case Opcodes.LSHL:
case Opcodes.ISHR:
case Opcodes.LSHR:
case Opcodes.IUSHR:
case Opcodes.LUSHR:
case Opcodes.IAND:
case Opcodes.LAND:
case Opcodes.IOR:
case Opcodes.LOR:
case Opcodes.IXOR:
case Opcodes.LXOR:
case Opcodes.LCMP:
case Opcodes.FCMPL:
case Opcodes.FCMPG:
case Opcodes.DCMPL:
case Opcodes.DCMPG:
// operand stack出栈:2,入栈:1
value2 = pop();
value1 = pop();
push(interpreter.binaryOperation(insn, value1, value2));
break;
case Opcodes.INEG:
case Opcodes.LNEG:
case Opcodes.FNEG:
case Opcodes.DNEG:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:1
push(interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop()));
break;
case Opcodes.IINC:
var = ((IincInsnNode) insn).var;
setLocal(var, interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, getLocal(var)));
break;
case Opcodes.I2L:
case Opcodes.I2F:
case Opcodes.I2D:
case Opcodes.L2I:
case Opcodes.L2F:
case Opcodes.L2D:
case Opcodes.F2I:
case Opcodes.F2L:
case Opcodes.F2D:
case Opcodes.D2I:
case Opcodes.D2L:
case Opcodes.D2F:
case Opcodes.I2B:
case Opcodes.I2C:
case Opcodes.I2S:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:1
push(interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop()));
break;
case Opcodes.IFEQ:
case Opcodes.IFNE:
case Opcodes.IFLT:
case Opcodes.IFGE:
case Opcodes.IFGT:
case Opcodes.IFLE:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPEQ:
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPNE:
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPLT:
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPGE:
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPGT:
case Opcodes.IF_ICMPLE:
case Opcodes.IF_ACMPEQ:
case Opcodes.IF_ACMPNE:
case Opcodes.PUTFIELD:
// operand stack出栈:2
value2 = pop();
value1 = pop();
interpreter.binaryOperation(insn, value1, value2);
break;
case Opcodes.GOTO:
break;
case Opcodes.JSR:
push(interpreter.newOperation(insn));
break;
case Opcodes.RET:
break;
case Opcodes.TABLESWITCH:
case Opcodes.LOOKUPSWITCH:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
case Opcodes.IRETURN:
case Opcodes.LRETURN:
case Opcodes.FRETURN:
case Opcodes.DRETURN:
case Opcodes.ARETURN:
value1 = pop();
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, value1);
interpreter.returnOperation(insn, value1, returnValue);
break;
case Opcodes.RETURN:
if (returnValue != null) {
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Incompatible return type");
}
break;
case Opcodes.GETSTATIC:
// operand stack入栈:1
push(interpreter.newOperation(insn));
break;
case Opcodes.PUTSTATIC:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
case Opcodes.GETFIELD:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:1
push(interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop()));
break;
case Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL:
case Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL:
case Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC:
case Opcodes.INVOKEINTERFACE:
executeInvokeInsn(insn, ((MethodInsnNode) insn).desc, interpreter);
break;
case Opcodes.INVOKEDYNAMIC:
executeInvokeInsn(insn, ((InvokeDynamicInsnNode) insn).desc, interpreter);
break;
case Opcodes.NEW:
// operand stack入栈:1
push(interpreter.newOperation(insn));
break;
case Opcodes.NEWARRAY:
case Opcodes.ANEWARRAY:
case Opcodes.ARRAYLENGTH:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:1
push(interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop()));
break;
case Opcodes.ATHROW:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
case Opcodes.CHECKCAST:
case Opcodes.INSTANCEOF:
// operand stack出栈:1,入栈:1
push(interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop()));
break;
case Opcodes.MONITORENTER:
case Opcodes.MONITOREXIT:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
case Opcodes.MULTIANEWARRAY:
// operand stack出栈:n,入栈:1
List<Value> valueList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = ((MultiANewArrayInsnNode) insn).dims; i > 0; --i) {
valueList.add(0, pop());
}
push(interpreter.naryOperation(insn, valueList));
break;
case Opcodes.IFNULL:
case Opcodes.IFNONNULL:
// operand stack出栈:1
interpreter.unaryOperation(insn, pop());
break;
default:
throw new AnalyzerException(insn, "Illegal opcode " + insn.getOpcode());
}
}
private void executeInvokeInsn(AbstractInsnNode insn, String methodDescriptor, Interpreter interpreter) {
ArrayList<Value> valueList = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加方法的参数
for (int i = Type.getArgumentTypes(methodDescriptor).length; i > 0; --i) {
valueList.add(0, pop());
}
// 考虑是否添加this变量
if (insn.getOpcode() != Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC && insn.getOpcode() != Opcodes.INVOKEDYNAMIC) {
valueList.add(0, pop());
}
if (Type.getReturnType(methodDescriptor) == Type.VOID_TYPE) {
// 返回void类型
interpreter.naryOperation(insn, valueList);
} else {
// 返回值不为void类型,需要将返回值加载到operand stack上
push(interpreter.naryOperation(insn, valueList));
}
}
}
initJumpTarget方法
initJumpTarget方法从两个方面来把握:它的作用是什么和它的调用时机是什么。
- 作用:提供一个修改当前Frame中值的机会,这样就可以对Frame的内容进行精细的管理。Overriding this method and changing the frame values allows implementing branch-sensitive analyses.
- 调用时机:遇到当前要执行的指令
- 首先,调用
init方法,复制当前指令执行之前的状态 - 其次,调用
execute方法,对当前的指令进行执行,Frame获得一个新的状态 - 再接着,判断一下当前指令是否是一个跳转指令(
if、switch),那么就会执行initJumpTarget方法,它允许我们对于当前Frame再进一步调整 - 最后,调用
merge方法,将当前的Frame“存储”起来。注意,这里不是直接存储,而是进行merge操作,就类似于将两个文件夹的内容放到一个文件夹里面。
- 首先,调用
public class Frame {
public void initJumpTarget(final int opcode, final LabelNode target) {
// Does nothing by default.
}
}
merge方法
下面的merge方法是将两个Frame对象的内容进行合并(merge),它会进一步的调用Interpreter.merge()方法。
public class Frame {
public boolean merge(Frame frame, final Interpreter interpreter) throws AnalyzerException {
if (numStack != frame.numStack) {
throw new AnalyzerException(null, "Incompatible stack heights");
}
boolean changed = false;
for (int i = 0; i < numLocals + numStack; ++i) {
Value v = interpreter.merge(values[i], frame.values[i]);
if (!v.equals(values[i])) {
values[i] = v;
changed = true;
}
}
return changed;
}
}
还有另外一个merge方法,我们故意将它省略了,因为它与jsr(subroutine)相关,而jsr指令不推荐使用了。
Interpreter类
与Frame类似,Interpreter也是一个泛型类,我们也可以将泛型V替换成Value值,以简化思考。
class info
第一个部分,Interpreter类是一个抽象类,它继承自Object类。
public abstract class Interpreter {
}
fields
第二个部分,Interpreter类定义的字段有哪些。
public abstract class Interpreter {
protected final int api;
}
constructors
第三个部分,Interpreter类定义的构造方法有哪些。
public abstract class Interpreter {
protected Interpreter(int api) {
this.api = api;
}
}
methods
第四个部分,Interpreter类定义的方法有哪些。
newValue相关方法
如果我们仔细观察下面几个方法,会发现它们都指向同一个方法,即Value newValue(Type)方法:该方法是将ASM当中的Type类型向Frame当中的Value类型进行映射。
public abstract class Interpreter {
public Value newParameterValue(boolean isInstanceMethod, int local, Type type) {
return newValue(type);
}
public Value newReturnTypeValue(Type type) {
return newValue(type);
}
public Value newEmptyValue(int local) {
return newValue(null);
}
public Value newExceptionValue(
TryCatchBlockNode tryCatchBlockNode,
Frame handlerFrame,
Type exceptionType) {
return newValue(exceptionType);
}
public abstract Value newValue(Type type);
}
具体来说,这几个方法的用途:
newParameterValue()方法:在方法头中,对“方法接收的参数类型”进行转换。newReturnTypeValue()方法:在方法头中,对“方法的返回值类型”进行转换。newEmptyValue()方法:将local variable当中某个位置设置成空值。newExceptionValue()方法:在方法体中,执行的时候,可能会出现异常,这里就是对“异常的类型”进行转换。
在local variable当中,为什么会有空值的出现呢?有两种情况:
- 第一种情况,假如local variable的总大小是10,而方法的接收参数只占前3个位置,那么剩下的7个位置的初始值就是空值。
- 第二种情况,在local variable当中,
long和double类型占用2个位置,在进行模拟的时候,第1个位置就记录了long和double类型,第2个位置就用空值来表示。
接着,我们解释一个这样的问题:为什么Value newValue(Type type)方法要将Type类型转换成Value类型?
| 领域 | ClassFile | ASM模拟类型或描述符 | ASM模拟Stack Frame(local variable+operand stack) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 类型 | Internal Name/Descriptor | Type | Value |
| 示例 | Ljava/lang/String; |
Type t = Type.getObjectType("java/lang/String"); |
BasicValue val = BasicValue.INT_VALUE; |
我们使用ASM编写代码,遇到的类型就是Type类型,接下来要做的就是模拟instruction执行过程中对local variable和operand stack的影响,因此需要将Type类型转换成Value类型。
举个例子,现在你持有中国的货币,接下来你想投资美国的市场,那么需要先将中国的货币兑换成美国的货币,然后才能去投资。
另外,我们要注意Type和Value类型的实例分别以_TYPE和_VALUE为结尾:
Type类型的实例:Type.VOID_TYPE、Type.BOOLEAN_TYPE、Type.CHAR_TYPE、Type.INT_TYPE、Type.FLOAT_TYPE、Type.LONG_TYPE、Type.DOUBLE_TYPE等。Value类型的实例:BasicValue.UNINITIALIZED_VALUE、BasicValue.INT_VALUE、BasicValue.FLOAT_VALUE、BasicValue.LONG_VALUE、BasicValue.DOUBLE_VALUE和BasicValue.REFERENCE_VALUE等。
除了以上的几个方法用到了newValue方法,还有哪些地方也会用到newValue方法:
- 在
BasicInterpreter类当中:ACONST_NULL指令:newValue(NULL_TYPE);CHECKCAST指令:newValue(Type.getObjectType(((TypeInsnNode) insn).desc));LDC指令:newValue(Type.getObjectType("java/lang/String"))GETFIELD指令:newValue(Type.getType(((FieldInsnNode) insn).desc))GETSTATIC指令:newValue(Type.getType(((FieldInsnNode) insn).desc))NEW指令:newValue(Type.getObjectType(((TypeInsnNode) insn).desc))NEWARRAY指令:newValue(Type.getType("[Z"))、newValue(Type.getType("[C"))等ANEWARRAY指令:newValue(Type.getType("[" + Type.getObjectType(((TypeInsnNode) insn).desc)))MULTIANEWARRAY指令:newValue(Type.getType(((MultiANewArrayInsnNode) insn).desc))INVOKEDYNAMIC指令:newValue(Type.getReturnType(((InvokeDynamicInsnNode) insn).desc))INVOKEVIRTUAL、INVOKESPECIAL、INVOKESTATIC、INVOKEINTERFACE指令:newValue(Type.getReturnType(((InvokeDynamicInsnNode) insn).desc))
- …(省略)
opcode相关方法
下面7个方法,就是结合指令(AbstractInsnNode类型)和多个元素值(Value类型)来计算出一个新的元素值(Value类型)。
public abstract class Interpreter {
public abstract Value newOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract Value copyOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, Value value) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract Value unaryOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, Value value) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract Value binaryOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, Value value1, Value value2) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract Value ternaryOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, Value value1, Value value2, Value value3) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract Value naryOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, List<Value> values) throws AnalyzerException;
public abstract void returnOperation(AbstractInsnNode insn, Value value, Value expected) throws AnalyzerException;
}
具体来说,这几个方法的作用:
newOperation()方法:处理opcode和0个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从0到1的操作。copyOperation()方法:处理opcode和1个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从1到1的操作。copy是“复制”,一个int类型的值,复制一份之后,仍然是int类型的值。unaryOperation()方法:处理opcode和1个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从1到1的操作。一个int类型的值,经过i2f指令运算,就会变成float类型的值。binaryOperation()方法:处理opcode和2个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从2到1的操作。ternaryOperation()方法:处理opcode和3个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从3到1的操作。naryOperation()方法:处理opcode和n个元素值(Value类型)之间的关系,这是一步从n到1的操作。returnOperation()方法:处理return的期望类型和实际类型之间的关系,这是一步从2到0的操作。
为什么有这些方法呢?因为opcode有200个左右,如果一个类里面定义200个方法,记忆起来就不太方便了。那么,按照“消耗”的元素值(Value类型)的数量多少,分成7个不同的方法,这就大大简化了方法的整体数量。
注意:在这里,我们用操作数(operand)和元素(element)表示不同的概念。
AbstractInsnNode类型,是指instruction,包含opcode和operand;这里的operand,体现为具体AbstractInsnNode类型的字段值。- 元素值(
Value类型),是指local variable和operand stack上某一个元素(element)的值。
instruction = opcode + operand
merge方法
这里是merge方法,它的作用是将两个Value值合并为一个新的Value值。
public abstract class Interpreter {
public abstract Value merge(Value value1, Value value2);
}
那么,为什么需要将两个Value值合并为一个新的Value值呢?我们举个例子:
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int a, int b) {
Object obj;
int c = a + b;
if (c > 10) {
obj = Integer.valueOf(20);
System.out.println(obj);
}
else {
obj = Float.valueOf(5);
System.out.println(obj);
}
int hashCode = obj.hashCode();
System.out.println(hashCode);
}
}
我们可以查看instruction对应的local variable和operand stack的变化:
test:(II)V
// {this, int, int} | {}
0000: iload_1 // {this, int, int} | {int}
0001: iload_2 // {this, int, int} | {int, int}
0002: iadd // {this, int, int} | {int}
0003: istore 4 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {}
0005: iload 4 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {int}
0007: bipush 10 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {int, int}
0009: if_icmple 19 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {}
0012: bipush 20 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {int}
0014: invokestatic #2 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {Integer}
0017: astore_3 // {this, int, int, Integer, int} | {}
0018: getstatic #3 // {this, int, int, Integer, int} | {PrintStream}
0021: aload_3 // {this, int, int, Integer, int} | {PrintStream, Integer}
0022: invokevirtual #4 // {this, int, int, Integer, int} | {}
0025: goto 16 // {} | {}
// {this, int, int, top, int} | {}
0028: ldc #5 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {float}
0030: invokestatic #6 // {this, int, int, top, int} | {Float}
0033: astore_3 // {this, int, int, Float, int} | {}
0034: getstatic #3 // {this, int, int, Float, int} | {PrintStream}
0037: aload_3 // {this, int, int, Float, int} | {PrintStream, Float}
0038: invokevirtual #4 // {this, int, int, Float, int} | {}
// {this, int, int, Object, int} | {}
0041: aload_3 // {this, int, int, Object, int} | {Object}
0042: invokevirtual #7 // {this, int, int, Object, int} | {int}
0045: istore 5 // {this, int, int, Object, int, int} | {}
0047: getstatic #3 // {this, int, int, Object, int, int} | {PrintStream}
0050: iload 5 // {this, int, int, Object, int, int} | {PrintStream, int}
0052: invokevirtual #8 // {this, int, int, Object, int, int} | {}
0055: return // {} | {}
在local variable当中,在(offset=17, local=3)的位置是Integer类型,在(offset=33, local=3)的位置是Float类型,它们merge之后是Object类型。
Value类
现在我们来看Value,它是一个接口,定义了一个getSize()方法。
public interface Value {
int getSize();
}
总结
本文内容总结如下:
- 第一点,
Frame类的从字段和方法两方面来把握:Frame类的字段,主要是values字段,用来记录local variable和operand stack的状态,其中存储的数据是Value类型。Frame类的方法,init、execute、initJumpTarget和merge方法,理解这几个方法,就能理解随着指令(instruction)的执行Frame的状态是如何变化的。
- 第二点,
Interpreter类的作用就像一个Value的工厂,要么从无到有的创建一个新的Value对象出来,要么多个Value对象合并成一个新的Value对象。 - 第三点,
Value是一个接口,它非常简单。
