在《Java ASM 系列一:Core API》当中,主要是对 Core API 进行了介绍; 但是,它并没有使用 Core API 来生成 Java 8 Lambda 表达式。
在本文当中,我们主要对 Java 8 Lambda 的两方面进行介绍:
- 第一方面,如何使用 ASM 生成 Lambda 表达式?
- 第二方面,探究 Lambda 表达式的实现原理是什么?
使用 ASM 生成 Lambda
预期目标
我们的预期目标是生成一个 HelloWorld 类,代码如下:
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test() {
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> func = Math::max;
Integer result = func.apply(10, 20);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
编码实现
在下面的代码中,我们重点关注两个点:
- 第一点,是
Handle实例的创建。 - 第二点,是
MethodVisitor.visitInvokeDynamicInsn()方法。
import lsieun.utils.FileUtils;
import org.objectweb.asm.*;
import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.*;
public class HelloWorldGenerateCore {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";
String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);
// (1) 生成 byte[]内容
byte[] bytes = dump();
// (2) 保存 byte[]到文件
FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes);
}
public static byte[] dump() throws Exception {
// (1) 创建 ClassWriter 对象
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
// (2) 调用 visitXxx()方法
cw.visit(V1_8, ACC_PUBLIC + ACC_SUPER, "sample/HelloWorld",
null, "java/lang/Object", null);
{
MethodVisitor mv1 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);
mv1.visitCode();
mv1.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 0);
mv1.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V", false);
mv1.visitInsn(RETURN);
mv1.visitMaxs(0, 0);
mv1.visitEnd();
}
{
MethodVisitor mv2 = cw.visitMethod(ACC_PUBLIC, "test", "()V", null, null);
mv2.visitCode();
// 第 1 点,Handle 实例的创建
Handle bootstrapMethodHandle = new Handle(H_INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/invoke/LambdaMetafactory", "metafactory",
"(Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandles$Lookup;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;" +
"Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandle;Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;)Ljava/lang/invoke/CallSite;", false);
// 第 2 点,MethodVisitor.visitInvokeDynamicInsn()方法的调用
mv2.visitInvokeDynamicInsn("apply", "()Ljava/util/function/BiFunction;",
bootstrapMethodHandle,
Type.getType("(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;"),
new Handle(H_INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Math", "max", "(II)I", false),
Type.getType("(Ljava/lang/Integer;Ljava/lang/Integer;)Ljava/lang/Integer;")
);
mv2.visitVarInsn(ASTORE, 1);
mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 1);
mv2.visitIntInsn(BIPUSH, 10);
mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);
mv2.visitIntInsn(BIPUSH, 20);
mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/Integer", "valueOf", "(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;", false);
mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEINTERFACE, "java/util/function/BiFunction", "apply",
"(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;", true);
mv2.visitTypeInsn(CHECKCAST, "java/lang/Integer");
mv2.visitVarInsn(ASTORE, 2);
mv2.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
mv2.visitVarInsn(ALOAD, 2);
mv2.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)V", false);
mv2.visitInsn(RETURN);
mv2.visitMaxs(0, 0);
mv2.visitEnd();
}
cw.visitEnd();
// (3) 调用 toByteArray()方法
return cw.toByteArray();
}
}
验证结果
接下来,我们来验证生成的 Lambda 表达式是否能够正常运行。
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class HelloWorldRun {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sample.HelloWorld");
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
Method m = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test");
m.invoke(obj);
}
}
探究 Lambda 的实现原理
简单来说,Lambda 表达式的内部原理,是借助于 Java ASM 生成匿名内部类来实现的。
追踪 Lambda
首先,我们使用 javap -v -p sample.HelloWorld 命令查看输出结果:
$ javap -v -p sample.HelloWorld
...
BootstrapMethods:
0: #28 invokestatic java/lang/invoke/LambdaMetafactory.metafactory:(
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandles$Lookup;
Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandle;
Ljava/lang/invok e/MethodType;
)Ljava/lang/invoke/CallSite;
Method arguments:
#29 (Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
#30 invokestatic java/lang/Math.max:(II)I
#31 (Ljava/lang/Integer;Ljava/lang/Integer;)Ljava/lang/Integer;
通过上面的输出结果,我们定位到 BootstrapMethods 的部分,
可以看到它使用了 java.lang.invoke.LambdaMetafactory 类的 metafactory() 方法。
至此,我们想表达的意思:Lambda 表达式是与 LambdaMetafactory.metafactory() 方法有关联关系的。
┌─── caller ──────────────────┼─── sample.HelloWorld
│
│ ┌─── invokedName ─────┼─── apply
│ │
LambdaMetafactory ───┼─── metafactory ───┼─── functional.interface ────┼─── invokedType ─────┼─── ()BiFunction
│ │
│ └─── samMethodType ───┼─── (Object, Object)Object
│
│ ┌─── implMethod ───────────────┼─── int Math.max(int,int)
└─── implementation.method ───┤
└─── instantiatedMethodType ───┼─── (Integer, Integer)Integer
在 IDE 当中,我们可以查看 LambdaMetafactory.metafactory() 方法,其内容如下:
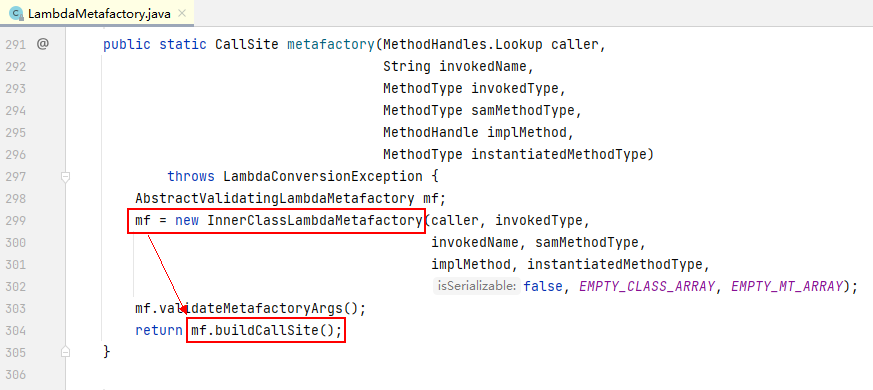
在上图中,我们可以看到 mf 指向一个 InnerClassLambdaMetafactory 的实例,并在最后调用了 buildCallSite() 方法。
接着,我们跳转到 java.lang.invoke.InnerClassLambdaMetafactory 类的 buildCallSite() 方法
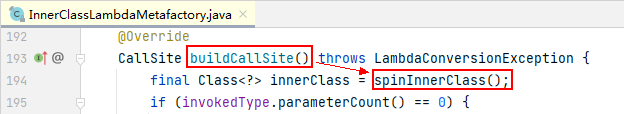
在 java.lang.invoke.InnerClassLambdaMetafactory 类的 spinInnerClass() 方法中,找到如下代码:
final byte[] classBytes = cw.toByteArray();
在其语句上,打一个断点:
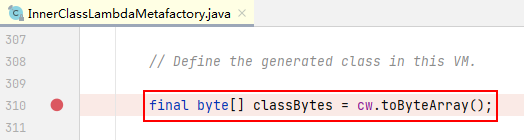
调试运行,然后使用如下表达式来查看 classBytes 的值:
Arrays.toString(classBytes)
其实,这里的 classBytes 就是生成的类文件的字节码内容,这样的字符串内容就是该字节码内容的另一种表现形式。
那么,拿到这样一个字符串内容之后,我们应该如何处理呢?
查看生成的类
在项目代码中,有一个 PrintASMTextLambda 类,它的作用就是将上述字符串内容的类信息打印出来。
import lsieun.utils.StringUtils;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassReader;
import org.objectweb.asm.util.Printer;
import org.objectweb.asm.util.Textifier;
import org.objectweb.asm.util.TraceClassVisitor;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PrintASMTextLambda {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// (1) 设置参数
String str = "[-54, -2, -70, -66, ...]";
byte[] bytes = StringUtils.array2Bytes(str);
int parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES | ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG;
// (2) 打印结果
Printer printer = new Textifier();
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out, true);
TraceClassVisitor traceClassVisitor = new TraceClassVisitor(null, printer, printWriter);
new ClassReader(bytes).accept(traceClassVisitor, parsingOptions);
}
}
我们可以将代表字节码内容的字符串放到上面代码的 str 变量中,然后运行 PrintASMTextLambda 可以得到如下结果:
// class version 52.0 (52)
// access flags 0x1030
final synthetic class sample/HelloWorld$$Lambda$1 implements java/util/function/BiFunction {
// access flags 0x2
private <init>()V
ALOAD 0
INVOKESPECIAL java/lang/Object.<init> ()V
RETURN
MAXSTACK = 1
MAXLOCALS = 1
// access flags 0x1
public apply(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
@Ljava/lang/invoke/LambdaForm$Hidden;()
ALOAD 1
CHECKCAST java/lang/Integer
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I
ALOAD 2
CHECKCAST java/lang/Integer
INVOKEVIRTUAL java/lang/Integer.intValue ()I
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Math.max (II)I
INVOKESTATIC java/lang/Integer.valueOf (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;
ARETURN
MAXSTACK = 2
MAXLOCALS = 3
}
通过上面的输出结果,我们可以看到:
- 第一点,当前类的名字叫
sample/HelloWorld$$Lambda$1。- 当前类带有
final和synthetic标识。 - 当前类实现了
java/util/function/BiFunction接口。
- 当前类带有
- 第二点,在
sample/HelloWorld$$Lambda$1类当中,它定义了一个构造方法(<init>()V)。 - 第三点,在
sample/HelloWorld$$Lambda$1类当中,它定义了一个apply方法(apply(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;)。- 这个
apply方法正是BiFunction接口中定义的方法。 apply方法的内部代码逻辑,是通过调用Math.max()方法来实现的;而Math::max正是 Lambda 表达式的内容。
- 这个
至此,我们可以知道:Lambda 表达式的实现,是由 JVM 调用 ASM 来实现的。
也就是说,JVM 使用 ASM 创建一个匿名内部类(sample/HelloWorld$$Lambda$1),
让该匿名内部类实现特定的接口(java/util/function/BiFunction),并在接口定义的方法(apply)实现中包含 Lambda 表达式的内容。
