对于 LocalVariablesSorter 类来说,它的特点是“可以引入新的局部变量,并且能够对局部变量重新排序”。
LocalVariablesSorter 类
class info
第一个部分,LocalVariablesSorter 类继承自 MethodVisitor 类。
- org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor
- org.objectweb.asm.commons.LocalVariablesSorter
- org.objectweb.asm.commons.GeneratorAdapter
- org.objectweb.asm.commons.AdviceAdapter
- org.objectweb.asm.commons.GeneratorAdapter
- org.objectweb.asm.commons.LocalVariablesSorter
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
}
fields
第二个部分,LocalVariablesSorter 类定义的字段有哪些。在理解 LocalVariablesSorter 类时,一个要记住的核心点:处理好”新变量“与”旧变量“的位置关系。换句话说,要给”新变量“在 local variables 当中找一个位置存储,”旧变量“也要在 local variables 当中找一个位置存储,它们的位置不能发生冲突。对于 local variables 当中某一个具体的位置,要么存储的是”新变量“,要么存储的是”旧变量“,不可能在同一个位置既存储”新变量“,又存储”旧变量“。
remappedVariableIndices字段,是一个int[]数组,其中所有元素的初始值为0。remappedVariableIndices字段的作用:只关心“旧变量”,它记录“旧变量”的新位置。remappedVariableIndices字段使用的算法,有点奇怪和特别。
remappedLocalTypes字段,将“旧变量”和“新变量”整合到一起之后,记录它们的类型信息。firstLocal字段,记录“方法体”中“第一个变量”在 local variables 当中的索引值,由于带有final标识,所以赋值之后,就不再发生变化了。nextLocal字段,记录 local variables 中可以未分配变量的位置,无论是“新变量”,还是“旧变量”,它们都是由nextLocal字段来分配位置;分配变量之后,nextLocal字段值会发生变化,重新指向 local variables 中未分配变量的位置。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
// The mapping from old to new local variable indices.
// A local variable at index i of size 1 is remapped to 'mapping[2*i]',
// while a local variable at index i of size 2 is remapped to 'mapping[2*i+1]'.
private int[] remappedVariableIndices = new int[40];
// The local variable types after remapping.
private Object[] remappedLocalTypes = new Object[20];
protected final int firstLocal;
protected int nextLocal;
}
constructors
第三个部分,LocalVariablesSorter 类定义的构造方法有哪些。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
public LocalVariablesSorter(final int access, final String descriptor, final MethodVisitor methodVisitor) {
this(Opcodes.ASM9, access, descriptor, methodVisitor);
}
protected LocalVariablesSorter(final int api, final int access, final String descriptor,
final MethodVisitor methodVisitor) {
super(api, methodVisitor);
nextLocal = (Opcodes.ACC_STATIC & access) == 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (Type argumentType : Type.getArgumentTypes(descriptor)) {
nextLocal += argumentType.getSize();
}
firstLocal = nextLocal;
}
}
methods
第四个部分,LocalVariablesSorter 类定义的方法有哪些。LocalVariablesSorter 类要处理好“新变量”与“旧变量”之间的关系。
newLocal method
newLocal() 方法就是为“新变量”来分配位置。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
public int newLocal(final Type type) {
Object localType;
switch (type.getSort()) {
case Type.BOOLEAN:
case Type.CHAR:
case Type.BYTE:
case Type.SHORT:
case Type.INT:
localType = Opcodes.INTEGER;
break;
case Type.FLOAT:
localType = Opcodes.FLOAT;
break;
case Type.LONG:
localType = Opcodes.LONG;
break;
case Type.DOUBLE:
localType = Opcodes.DOUBLE;
break;
case Type.ARRAY:
localType = type.getDescriptor();
break;
case Type.OBJECT:
localType = type.getInternalName();
break;
default:
throw new AssertionError();
}
int local = newLocalMapping(type);
setLocalType(local, type);
setFrameLocal(local, localType);
return local;
}
protected int newLocalMapping(final Type type) {
int local = nextLocal;
nextLocal += type.getSize();
return local;
}
protected void setLocalType(final int local, final Type type) {
// The default implementation does nothing.
}
private void setFrameLocal(final int local, final Object type) {
int numLocals = remappedLocalTypes.length;
if (local >= numLocals) { // 这里是处理分配空间不足的情况
Object[] newRemappedLocalTypes = new Object[Math.max(2 * numLocals, local + 1)];
System.arraycopy(remappedLocalTypes, 0, newRemappedLocalTypes, 0, numLocals);
remappedLocalTypes = newRemappedLocalTypes;
}
remappedLocalTypes[local] = type; // 真正的处理逻辑只有这一句代码
}
}
local variables method
visitVarInsn() 和 visitIincInsn() 方法就是为“旧变量”来重新分配位置,这两个方法都会去调用 remap(var, type) 方法。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
@Override
public void visitVarInsn(final int opcode, final int var) {
Type varType;
switch (opcode) {
case Opcodes.LLOAD:
case Opcodes.LSTORE:
varType = Type.LONG_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.DLOAD:
case Opcodes.DSTORE:
varType = Type.DOUBLE_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.FLOAD:
case Opcodes.FSTORE:
varType = Type.FLOAT_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.ILOAD:
case Opcodes.ISTORE:
varType = Type.INT_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.ALOAD:
case Opcodes.ASTORE:
case Opcodes.RET:
varType = OBJECT_TYPE;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid opcode " + opcode);
}
super.visitVarInsn(opcode, remap(var, varType));
}
@Override
public void visitIincInsn(final int var, final int increment) {
super.visitIincInsn(remap(var, Type.INT_TYPE), increment);
}
private int remap(final int var, final Type type) {
// 第一部分,处理方法的输入参数
if (var + type.getSize() <= firstLocal) {
return var;
}
// 第二部分,处理方法体内定义的局部变量
int key = 2 * var + type.getSize() - 1;
int size = remappedVariableIndices.length;
if (key >= size) { // 这段代码,主要是处理分配空间不足的情况。我们可以假设分配的空间一直是足够的,那么可以忽略此段代码
int[] newRemappedVariableIndices = new int[Math.max(2 * size, key + 1)];
System.arraycopy(remappedVariableIndices, 0, newRemappedVariableIndices, 0, size);
remappedVariableIndices = newRemappedVariableIndices;
}
int value = remappedVariableIndices[key];
if (value == 0) { // 如果是 0,则表示还没有记录下来
value = newLocalMapping(type);
setLocalType(value, type);
remappedVariableIndices[key] = value + 1;
} else { // 如果不是 0,则表示有具体的值
value--;
}
return value;
}
protected int newLocalMapping(final Type type) {
int local = nextLocal;
nextLocal += type.getSize();
return local;
}
}
工作原理
对于 LocalVariablesSorter 类的工作原理,主要依赖于三个字段:firstLocal、nextLocal 和 remappedVariableIndices 字段。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
// The mapping from old to new local variable indices.
// A local variable at index i of size 1 is remapped to 'mapping[2*i]',
// while a local variable at index i of size 2 is remapped to 'mapping[2*i+1]'.
private int[] remappedVariableIndices = new int[40];
protected final int firstLocal;
protected int nextLocal;
}
首先,我们来看一下 firstLocal 和 nextLocal 初始化,它发生在 LocalVariablesSorter 类的构造方法中。其中,firstLocal 是一个 final 类型的字段,一次赋值之后就不能变化了;而 nextLocal 字段的取值可以继续变化。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
protected LocalVariablesSorter(final int api, final int access, final String descriptor,
final MethodVisitor methodVisitor) {
super(api, methodVisitor);
nextLocal = (Opcodes.ACC_STATIC & access) == 0 ? 1 : 0; // 首先,判断是不是静态方法
for (Type argumentType : Type.getArgumentTypes(descriptor)) { // 接着,循环方法接收的参数
nextLocal += argumentType.getSize();
}
firstLocal = nextLocal; // 最后,为 firstLocal 字段赋值。
}
}
对于上面的代码,主要是对两方面内容进行判断:
- 第一方面,是否需要处理
this变量。 - 第二方面,对方法接收的参数进行处理。
在执行完 LocalVariablesSorter 类的构造方法后,firstLocal 和 nextLocal 的值是一样的,其值表示下一个方法体中的变量在 local variables 当中的位置。接下来,就是该考虑第三方面的事情了:
- 第三方面,方法体内定义的变量。对于这些变量,又分成两种情况:
- 第一种情况,程序代码中原来定义的变量。
- 第二种情况,程序代码中新定义的变量。
对于 LocalVariablesSorter 类来说,它要处理的一个关键性的工作,就是处理好“旧变量”和“新变量”之间的关系。其实,不管是“新变量”,还是“旧变量”,它都是通过 newLocalMapping(type) 方法来找到自己的位置。newLocalMapping(type) 方法的逻辑就是“先到先得”。有一个形象的例子,可以帮助我们理解 newLocalMapping(type) 方法的作用。高考之后,过一段时间,大学就会开学,新生就会来报到;不管新学生来自于什么地方,第一个来到学校的学生就分配 001 的编号,第二个来到学校的学生就分配 002 的编号,依此类推。
我们先来说明第二种情况,也就是在程序代码中添加新的变量。
添加新变量
如果要添加新的变量,那么需要调用 newLocal(type) 方法。
- 在
newLocal(type)方法中,它会进一步调用newLocalMapping(type)方法; - 在
newLocalMapping(type)方法中,首先会记录nextLocal的值到local局部变量中,接着会更新nextLocal的值(即加上type.getSize()的值),最后返回local的值。那么,local的值就是新变量在 local variables 当中存储的位置。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
public int newLocal(final Type type) {
int local = newLocalMapping(type);
return local;
}
protected int newLocalMapping(final Type type) {
int local = nextLocal;
nextLocal += type.getSize();
return local;
}
}
处理旧变量
如果要处理“旧变量”,那么需要调用 visitVarInsn(opcode, var) 或 visitIincInsn(var, increment) 方法。在这两个方法中,会进一步调用 remap(var, type) 方法。其中,remap(var, type) 方法的主要作用,就是实现“旧变量”的原位置向新位置的映射。
public class LocalVariablesSorter extends MethodVisitor {
@Override
public void visitVarInsn(final int opcode, final int var) {
Type varType;
switch (opcode) {
case Opcodes.LLOAD:
case Opcodes.LSTORE:
varType = Type.LONG_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.DLOAD:
case Opcodes.DSTORE:
varType = Type.DOUBLE_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.FLOAD:
case Opcodes.FSTORE:
varType = Type.FLOAT_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.ILOAD:
case Opcodes.ISTORE:
varType = Type.INT_TYPE;
break;
case Opcodes.ALOAD:
case Opcodes.ASTORE:
case Opcodes.RET:
varType = OBJECT_TYPE;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid opcode " + opcode);
}
super.visitVarInsn(opcode, remap(var, varType));
}
@Override
public void visitIincInsn(final int var, final int increment) {
super.visitIincInsn(remap(var, Type.INT_TYPE), increment);
}
private int remap(final int var, final Type type) {
// 第一部分,处理方法的输入参数
if (var + type.getSize() <= firstLocal) {
return var;
}
// 第二部分,处理方法体内定义的局部变量
int key = 2 * var + type.getSize() - 1;
int value = remappedVariableIndices[key];
if (value == 0) { // 如果是 0,则表示还没有记录下来
value = newLocalMapping(type);
remappedVariableIndices[key] = value + 1;
} else { // 如果不是 0,则表示有具体的值
value--;
}
return value;
}
protected int newLocalMapping(final Type type) {
int local = nextLocal;
nextLocal += type.getSize();
return local;
}
}
在 remap(var, type) 方法中,有两部分主要逻辑:
- 第一部分,是处理方法的输入参数。方法接收的参数,它们在 local variables 当中的索引位置是不会变化的,所以处理起来也比较简单,直接返回
var的值。 - 第二部分,是处理方法体内定义的局部变量。在这个部分,就是
remappedVariableIndices字段发挥作用的地方,也会涉及到nextLocal字段。
在 remap(var, type) 方法中,我们重点关注第二部分,代码处理的步骤是:
- 第一步,计算出
remappedVariableIndices字段的一个索引值key,即int key = 2 * var + type.getSize() - 1。假设有一个变量的索引是i,如果该变量的大小是 1,那么它在remappedVariableIndices字段中的索引位置是2*i;如果该变量(long或double类型)的大小是 2,那么它在remappedVariableIndices字段中的索引位置是2*i+1。 - 第二步,根据
key值,取出remappedVariableIndices字段当中的value值。大家注意,int[] remappedVariableIndices = new int[40],也就是说,remappedVariableIndices字段是一个数组,所有元素的默认值是0。- 如果
value的值是0,说明还没有记录“旧变量”的新位置;那么,就通过value = newLocalMapping(type)计算出新的位置,将value + 1赋值给remappedVariableIndices字段中key位置。 - 如果
value的值不是0,说明已经记录“旧变量”的新位置;这个时候,要进行value--操作。
- 如果
- 第三步,返回
value的值。那么,这个value值就是“旧变量”的新位置。
在上面的代码当中,我们可以看到 remap 方法里有 value + 1 和 value-- 的代码:
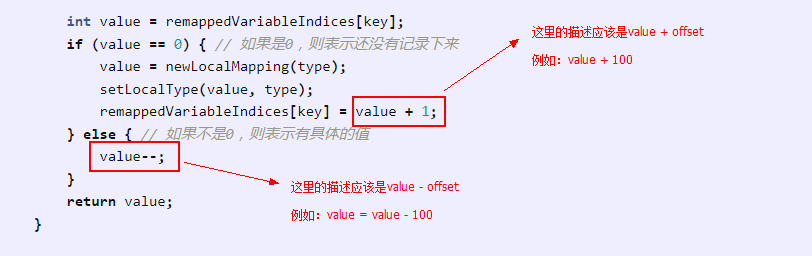
为什么进行这样的处理呢?我们来思考这样的问题:当创建一个新的 int[] 时,其中的每一个元素的默认值都是 0;在 local variable 当中,0 是一个有效的索引值;
那么,如果从 int[] 数组当中取出一个元素,它的值是 0,那它是代表元素的“默认值”,还是 local variable 当中的一个有效的索引值 0 呢?
为了进行区分,它加一个 offset 值,而在代码中这个 offset 的值是 1,我觉得,将 offset 取值成 100 也能得到一个正确的结果。
示例
预期目标
假如有一个 HelloWorld 类,代码如下:
import java.util.Random;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int a, int b) throws Exception {
int c = a + b;
int d = c * 10;
Random rand = new Random();
int value = rand.nextInt(d);
Thread.sleep(value);
}
}
我们想实现的预期目标:添加一个新的局部变量 t,然后使用变量 t 计算方法的运行时间。
import java.util.Random;
public class HelloWorld {
public void test(int a, int b) throws Exception {
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int c = a + b;
int d = c * 10;
Random rand = new Random();
int value = rand.nextInt(d);
Thread.sleep(value);
t = System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
System.out.println("test method execute: " + t);
}
}
编码实现
下面的 MethodTimerAdapter3 类继承自 LocalVariablesSorter 类。
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Type;
import org.objectweb.asm.commons.LocalVariablesSorter;
import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.*;
public class MethodTimerVisitor3 extends ClassVisitor {
public MethodTimerVisitor3(int api, ClassVisitor cv) {
super(api, cv);
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
if (mv != null && !"<init>".equals(name) && !"<clinit>".equals(name)) {
boolean isAbstractMethod = (access & ACC_ABSTRACT) != 0;
boolean isNativeMethod = (access & ACC_NATIVE) != 0;
if (!isAbstractMethod && !isNativeMethod) {
mv = new MethodTimerAdapter3(api, access, name, descriptor, mv);
}
}
return mv;
}
private static class MethodTimerAdapter3 extends LocalVariablesSorter {
private final String methodName;
private final String methodDesc;
private int slotIndex;
public MethodTimerAdapter3(int api, int access, String name, String descriptor, MethodVisitor methodVisitor) {
super(api, access, descriptor, methodVisitor);
this.methodName = name;
this.methodDesc = descriptor;
}
@Override
public void visitCode() {
// 首先,实现自己的逻辑
slotIndex = newLocal(Type.LONG_TYPE);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LSTORE, slotIndex);
// 其次,调用父类的实现
super.visitCode();
}
@Override
public void visitInsn(int opcode) {
// 首先,实现自己的逻辑
if ((opcode >= IRETURN && opcode <= RETURN) || opcode == ATHROW) {
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LLOAD, slotIndex);
mv.visitInsn(LSUB);
mv.visitVarInsn(LSTORE, slotIndex);
mv.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
mv.visitTypeInsn(NEW, "java/lang/StringBuilder");
mv.visitInsn(DUP);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "<init>", "()V", false);
mv.visitLdcInsn(methodName + methodDesc + " method execute: ");
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LLOAD, slotIndex);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(J)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", false);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);
}
// 其次,调用父类的实现
super.visitInsn(opcode);
}
}
}
需要注意的是,我们使用的是 mv.visitVarInsn(opcode, var) 方法,而不是使用 super.visitVarInsn(opcode, var) 方法。为什么要使用 mv,而不使用 super 呢?因为使用 super.visitVarInsn(opcode, var) 方法,实质上是调用了 LocalVariablesSorter.visitVarInsn(opcode, var),它会进一步调用 remap(var, type) 方法,这就可能导致新添加的变量在 local variables 中的位置发生“位置偏移”。
下面的 MethodTimerAdapter4 类继承自 AdviceAdapter 类。
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Type;
import org.objectweb.asm.commons.AdviceAdapter;
import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.ACC_ABSTRACT;
import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.ACC_NATIVE;
public class MethodTimerVisitor4 extends ClassVisitor {
public MethodTimerVisitor4(int api, ClassVisitor classVisitor) {
super(api, classVisitor);
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
if (mv != null) {
boolean isAbstractMethod = (access & ACC_ABSTRACT) != 0;
boolean isNativeMethod = (access & ACC_NATIVE) != 0;
if (!isAbstractMethod && !isNativeMethod) {
mv = new MethodTimerAdapter4(api, mv, access, name, descriptor);
}
}
return mv;
}
private static class MethodTimerAdapter4 extends AdviceAdapter {
private int slotIndex;
public MethodTimerAdapter4(int api, MethodVisitor mv, int access, String name, String descriptor) {
super(api, mv, access, name, descriptor);
}
@Override
protected void onMethodEnter() {
slotIndex = newLocal(Type.LONG_TYPE);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LSTORE, slotIndex);
}
@Override
protected void onMethodExit(int opcode) {
if ((opcode >= IRETURN && opcode <= RETURN) || opcode == ATHROW) {
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, "java/lang/System", "currentTimeMillis", "()J", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LLOAD, slotIndex);
mv.visitInsn(LSUB);
mv.visitVarInsn(LSTORE, slotIndex);
mv.visitFieldInsn(GETSTATIC, "java/lang/System", "out", "Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
mv.visitTypeInsn(NEW, "java/lang/StringBuilder");
mv.visitInsn(DUP);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "<init>", "()V", false);
mv.visitLdcInsn(getName() + methodDesc + " method execute: ");
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);
mv.visitVarInsn(LLOAD, slotIndex);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "append", "(J)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;", false);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/lang/StringBuilder", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", false);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/io/PrintStream", "println", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", false);
}
}
}
}
进行转换
import lsieun.utils.FileUtils;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassReader;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
public class HelloWorldTransformCore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";
String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);
byte[] bytes1 = FileUtils.readBytes(filepath);
//(1)构建 ClassReader
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes1);
//(2)构建 ClassWriter
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
//(3)串连 ClassVisitor
int api = Opcodes.ASM9;
ClassVisitor cv = new MethodTimerVisitor4(api, cw);
//(4)结合 ClassReader 和 ClassVisitor
int parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;
cr.accept(cv, parsingOptions);
//(5)生成 byte[]
byte[] bytes2 = cw.toByteArray();
FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes2);
}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloWorld instance = new HelloWorld();
instance.test(10, 20);
}
}
总结
本文对 LocalVariablesSorter 类进行介绍,内容总结如下:
- 第一点,了解
LocalVariablesSorter类的各个部分,都有哪些信息。 - 第二点,理解
LocalVariablesSorter类的工作原理。 - 第三点,如何使用
LocalVariablesSorter类添加新的变量。
