如何清空方法体
在有些情况下,我们可能想清空整个方法体的内容,那该怎么做呢?其实,有两个思路。
- 第一种思路,就是将 instruction 一条一条的移除掉,直到最后只剩下 return 语句。(不推荐)
- 第二种思路,就是忽略原来的方法体,重新生成一个新的方法体。(推荐使用)
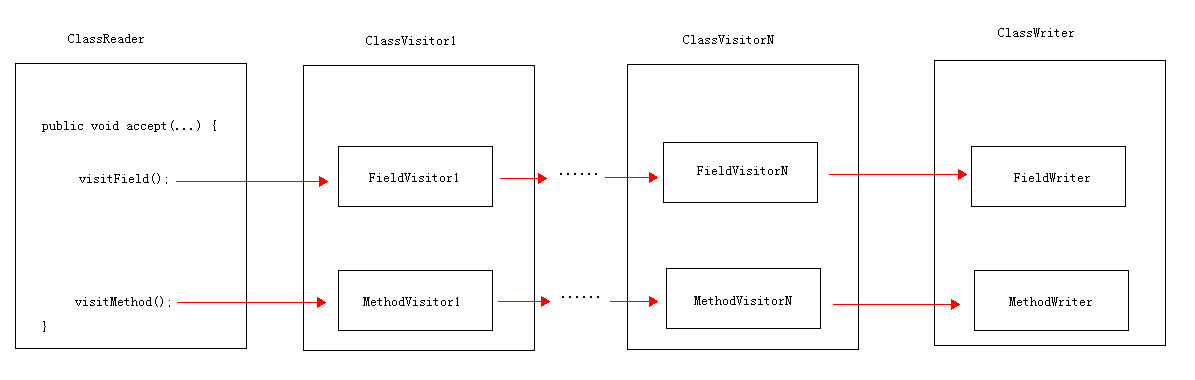
对于第二种思路,“忽略原来的方法体,重新生成一个新的方法体”,想法很好,具体如何实现呢?假设有一个中间的 MethodVisitor 来负责做这个工作,通过两个步骤来实现:
- 第一步,对于它“前面”的
MethodVisitor,它返回null值,就相当于原来的方法丢失了; - 第二步,对于它“后面”的
MethodVisitor,它添加同名、同类型的方法,然后生成新的方法体,这就相当于又添加了一个新的方法。
需要注意的一点:清空方法体,并不是一条 instruction 也没有,它至少要有一条 return 语句。
- 如果方法返回值是
void类型,那至少要有一个 return; - 如果方法返回值不是
void类型(例如,int、String),这个时候,就要考虑返回一个什么样的值比较合适了。
同时,我们也要计算 local variables 和 operand stack 的大小:
- 计算 local variables 的大小。在 local variables 中,主要是用于存储
this变量和方法的参数,只要计算this和方法参数的大小就可以了。 - 计算 operand stack 的大小。
- 如果方法有返回值,则需要先放到 operand stack 上去,再进行返回,那么 operand stack 的大小与返回值的类型密切相关;
- 如果方法没有返回值,清空方法体后,那么 operand stack 的大小为
0。
计算 local variables 和 operand stack 的大小,可以由我们自己编码来实现,也可以由 ASM 帮助我们实现。
示例:绕过验证机制
预期目标
假如有一个 HelloWorld 类,代码如下:
public class HelloWorld {
public void verify(String username, String password) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if ("tomcat".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("username or password is not correct");
}
}
我们想实现的预期目标:清空 verify 方法的方法体,无论输入什么样的值,它都不会报错。
public class HelloWorld {
public void verify(String username, String password) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return;
}
}
编码实现
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
import org.objectweb.asm.Type;
import static org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes.*;
public class MethodEmptyBodyVisitor extends ClassVisitor {
private String owner;
private final String methodName;
private final String methodDesc;
public MethodEmptyBodyVisitor(int api, ClassVisitor classVisitor, String methodName, String methodDesc) {
super(api, classVisitor);
this.methodName = methodName;
this.methodDesc = methodDesc;
}
@Override
public void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {
super.visit(version, access, name, signature, superName, interfaces);
this.owner = name;
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, descriptor, signature, exceptions);
if (mv != null && methodName.equals(name) && methodDesc.equals(descriptor)) {
boolean isAbstractMethod = (access & ACC_ABSTRACT) != 0;
boolean isNativeMethod = (access & ACC_NATIVE) != 0;
if (!isAbstractMethod && !isNativeMethod) {
generateNewBody(mv, owner, access, name, descriptor);
return null;
}
}
return mv;
}
protected void generateNewBody(MethodVisitor mv, String owner, int methodAccess, String methodName, String methodDesc) {
// (1) method argument types and return type
Type t = Type.getType(methodDesc);
Type[] argumentTypes = t.getArgumentTypes();
Type returnType = t.getReturnType();
// (2) compute the size of local variable and operand stack
boolean isStaticMethod = ((methodAccess & Opcodes.ACC_STATIC) != 0);
int localSize = isStaticMethod ? 0 : 1;
for (Type argType : argumentTypes) {
localSize += argType.getSize();
}
int stackSize = returnType.getSize();
// (3) method body
mv.visitCode();
if (returnType.getSort() == Type.VOID) {
mv.visitInsn(RETURN);
}
else if (returnType.getSort() >= Type.BOOLEAN && returnType.getSort() <= Type.INT) {
mv.visitInsn(ICONST_1);
mv.visitInsn(IRETURN);
}
else if (returnType.getSort() == Type.LONG) {
mv.visitInsn(LCONST_0);
mv.visitInsn(LRETURN);
}
else if (returnType.getSort() == Type.FLOAT) {
mv.visitInsn(FCONST_0);
mv.visitInsn(FRETURN);
}
else if (returnType.getSort() == Type.DOUBLE) {
mv.visitInsn(DCONST_0);
mv.visitInsn(DRETURN);
}
else {
mv.visitInsn(ACONST_NULL);
mv.visitInsn(ARETURN);
}
mv.visitMaxs(stackSize, localSize);
mv.visitEnd();
}
}
进行转换
import lsieun.utils.FileUtils;
import org.objectweb.asm.*;
public class HelloWorldTransformCore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String relative_path = "sample/HelloWorld.class";
String filepath = FileUtils.getFilePath(relative_path);
byte[] bytes1 = FileUtils.readBytes(filepath);
//(1)构建 ClassReader
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(bytes1);
//(2)构建 ClassWriter
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
//(3)串连 ClassVisitor
int api = Opcodes.ASM9;
ClassVisitor cv = new MethodEmptyBodyVisitor(api, cw, "verify", "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V");
//(4)结合 ClassReader 和 ClassVisitor
int parsingOptions = ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG | ClassReader.SKIP_FRAMES;
cr.accept(cv, parsingOptions);
//(5)生成 byte[]
byte[] bytes2 = cw.toByteArray();
FileUtils.writeBytes(filepath, bytes2);
}
}
验证结果
public class HelloWorldRun {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloWorld instance = new HelloWorld();
instance.verify("jerry", "123");
}
}
总结
本文主要对清空方法体进行了介绍,内容总结如下:
- 第一点,清空方法体,它的思路是,忽略原来的方法体,然后重新生成新的方法体。
- 第二点,清空方法体过程中,要注意的事情是,方法体当中要包含 return 相关的语句,同时要计算 local variables 和 operand stack 的大小。
